1. INTRODUCTION
In 2015-2016, the Brazilian economy plunged into its most severe recession since the post-war, and recovery has been sluggish. The decrease in Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in 2015 and 2016 was over 3.0% each year, and the average increase in 2017-2019 was only 1.3% per year. Not only the shrinking of gdp has been accentuated compared to past experiences, as it occurred without a balance of payments crisis. Most authors argue that the causes of the recent recession in Brazil are related to the lack of success of the macroeconomic policies to sustain aggregate demand, mainly after the 2011-2012 European crisis1. In this paper, we will add that the Brazilian economy was in an ascending phase of an investment cycle in 2008, and as a result, the change in the external environment after the international financial crisis in 2008 and in economic policy orientation from 2011 onwards negatively impacted the balance sheet of non-financial firms. Indeed, in 2019, the investment rate was only 15.4% (nominal terms). Therefore, the poor recent growth performance of the Brazilian economy shows the difficulty of resuming the investment rate to its level before the Brazilian recession (19.9% in 2014).
Brazilian recession should be analyzed considering the asymmetrical financial integration, which narrows policy space, turning the economy more vulnerable to external events. Therefore, even in the absence of an external shock, changes in the external environment turn economic agents more precautious, which in part can explain a slow recovery. In fact, in Feijo, Lamônica, and Lima (2020), industrial firms’ financial fragility was explained with an econometric model using instrumental variables in two stages applied in a cointegration panel model. The importance of the exchange rate volatility and the deceleration in the world income was captured as instruments to explain the cointegrated model’s explanatory variables. In this paper, we will forward the investigation about the financial fragility of industrial firms assuming that the deceleration in the investment rate after 2014 can be explained because the economic measures implemented to sustain profit margins from 2011 onwards were not enough to counterbalance the deceleration in the aggregate demand and the rise in financial costs. Following Minsky’s financial fragility hypothesis, this paper’s main contribution is to argue that the deceleration of aggregate demand deteriorates firms’ balance sheet because it increases the weight of private debts and negatively affects investment plans. Through an econometric model, we observe the coevolution of macroeconomic variables and the building up of industrial firms’ financial fragility to explain the Brazilian economy’s slowdown in the 2010s.
Besides this introduction, this paper is divided into the following sections. The first section briefly discusses Minsky’s financial fragility hypothesis. The second section presents a discussion about the evolution of the Brazilian economy in the 2010s, emphasising the behaviour of capital formation in a context of reduced aggregate demand prospects. To investigate the evolution of the financial fragility of industrial firms, the third section proposes an aggregate index to capture the financial fragility of industrial firms2. The next section presents an econometric exercise to explain the determinants of the financial fragility index of industrial firms in the period 2007-2016. With this exercise, we can show that the deterioration of the capacity of industrial firms to generate enough internal funds to face debt commitments can be explained by macroeconomic variables, such as the evolution of credit operations in relation to total investment, the nominal interest rate and by sectoral variables such as the wage costs, the composition of receipts and the industrial investment rate. The last section concludes the paper.
2. MINSKY’S FINANCIAL FRAGILITY HYPOTHESIS
Minsky’s financial fragility hypothesis (1986) is developed for an economic environment with a sophisticated and complex financial system. The financial interaction among economic agents describes how moments of stability and economic turbulence are recurrent. Minsky assumes that the financial fragility results from the endogenous tendency of market economies to expand based on an increase in indebtedness and the possible difficulty that different economic units in the real and financial sectors have to fulfil past debt obligations. The key assumption about economic agents’ behaviour is that decisions are guided by expectations formed under non-probabilistic uncertainty. Therefore, the endogenous character of the business cycle described by Minsky’s theoretical view can be understood as a rational reaction of economic agents in defence of their wealth.
Minsky’s financial fragility hypothesis presupposes that wealth accumulation is not limited to expanding the stock of productive capital, but also accumulating a diversified basket of assets combining the yields of productive and financial capital3. Minsky (1977, p. 23), describes modern capitalist economies as “… a paper world. The viability of this paper world rests upon the cash flows (or gross profits after out-of-pocket costs and taxes) that business organizations, households, and governmental bodies… receive as a result of the income-generating process.” As explained by Kregel and Burlamaqui (2005, p. 147), with the expression ‘paper world’, “Minsky emphasises the need to incorporate real-world phenomena fully -and especially finance- into the core of economic analysis, to grasp the intrinsically unstable nature of capitalist economies” (italics in the original). In this sense, a ‘paper world’ implies that financial assets meet both the criteria of offering profitability and liquidity, reducing, therefore, the degree of uncertainty involved in the process of accumulation of capital in fixed assets.
According to the financial fragility hypothesis, decisions that involve financial resources in large volumes and a long period to mature end up depending mainly on decisions taken by financial firms to expand financing to meet the demand for capital goods or to roll over the accumulated weight of debt. In times of optimistic expectations and growing aggregate demand agents can count on the expected income to cover their debt commitments. They can also rely on external financing through the issuance of shares, sale of assets or simply through financial loans granted by banks and other financial institutions. However, a deterioration of expectations will point toward a reduction in the supply of new loans and the raising of interest rates. The upward phase of the business cycle can be described as the one in which economic units move from more conservative postures in their balance sheets to more speculative postures. While the financial conditions feed positive expectations about the realization of expected profits, liquidity is plentiful. Once financial conditions change more indebted units face more difficulty in rolling over their past commitments and the reverse of the expansionary phase is observed4.
Therefore, boom periods translate into an expansion of the balance sheets of financial and non-financial firms, and periods of recession translate into a shrinking in their balance sheets. This movement in the leverage of firms, in its turn, generates instability in the economy, which is translated, according to the availability of credit, into the economic activity. In Minsky’s view, the contraction of credit has a medium-term or more permanent negative impact on the growth trajectory of an economy through the contraction of investment in fixed capital and loss of human capital5.
3. BRAZILIAN ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE AND THE INVESTMENT CYCLE
The starting point to discuss the evolution of the Brazilian economy to evaluate the recent investment cycle will consider two periods. From 2000 to 2010, the Brazilian economy faced favourable external conditions and a well-succeeded income distribution policy, which both contributed to stimulate the investment rate (Table 1). This is also the period when the macroeconomic policy arrangement based on the flexible exchange rate, inflation targeting, and primary fiscal surpluses, known as the macroeconomic tripod, is consolidated. Although this policy arrangement established a relatively high level of nominal and real interest rate and an appreciation trend of the real exchange rate, which induced the substitution of domestic goods for imported goods and led to a process of de-industrialization6, domestic demand expanded. Besides, the improvement on the terms of trade in the 2003-2008 period, domestic demand was also fueled by the increase of the real minimum wage, an increase in employment rates and the supply of consumer credit. The second period starts in 2011 when the perception that the recovery of the world economy would be slow and, domestically, there was a shift of macroeconomic policies from the incentive to aggregate demand to supply-side incentives. The deterioration on the terms of trade from 2012 onwards and the deceleration of domestic growth rates led to two years of deep recession (2015-2016) with investment rates dropping steadily7.
Table 1 Average per year growth rates of gdp and components of aggregate demand (%), 2000-2019
| GDP | Private consumption | Government consumption | |
| 2000-2010 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 2.7 |
| 2011-2019 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 0.5 |
| Gross fixed capital formation | Exports | Imports | |
| 2000-2010 | 5.0 | 6.9 | 8.2 |
| 2011-2019 | -1.5 | 2.2 | 0.7 |
Source: Brazilian Statistical Office, Quarterly National Accounts.
Table 1 presents the growth rates of GDP and the components of aggregate demand for the two periods, and the point to highlight is the behaviour of gross capital formation. During the 2000-2010 period, gross investment in fixed capital grew on average 5.0% a year. The investment rate was on average 18.2% of GDP (nominal terms). In the next period, when GDP growth was only 0.7% on average a year, gross capital formation registered a negative rate of growth of 1.5% a year, and the investment rate was 17.8% on average (2011-2019).
An illustration of the evolution of the investment rate is shown in Figure 1. The investment rate started to increase in 2004-2005 and steadily augmented until 2008. In 2009 gross fixed capital formation decreased 2.1% and in 2010, due to economic measures to stimulate aggregate expending, investment increased 17.9%. The investment rate was kept around 20.7% until 2013, but the domestic conditions to finance long-term investment and the entrepreneurial expectations were not the same as they were in 2008. In this sense, the rate of investment started to decelerate from 2013 onwards.
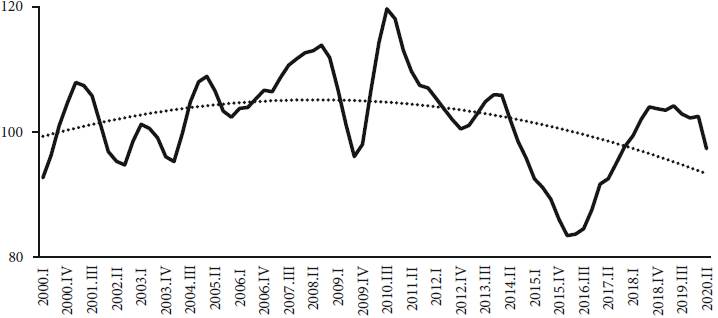
Source: Brazilian Statistical Office, Quarterly National Accounts.
Figure 1 Index of 12 months moving average of Gross Fixed Capital Formation in volume (1995 prices) seasonally adjusted and trend line (polynomial of order 2 - dotted line), 2000-2020
The expressive increase in the investment rate from the mid-2000s on was a result of the optimistic expectations in the potential growth rate of the Brazilian economy directly related both to the improvement on the terms of trade (2003-2008) and also the expansion of the domestic market, due to policies to sustain real gains of the minimum wage and the program of income transfer. A favourable scenario was set up8 so that spontaneous optimism would emerge. However, the sudden change in the external scenario in 2008 and the perspective of a long-lasting world recession, in line with Minsky’s description of the business cycle, hurt business expectations, and the firms’ financial balance sheet started to deteriorate.
Figure 2 shows the evolution in nominal terms of the fixed gross capital formation and non financial credit operations and it shows the critical moment when a growing number of firms might have been disappointed in their revenue expectations to face up their debt commitments. In this case, they might have been compelled to refinance their debts under worse and riskier conditions. It should be added that the basic interest rate started to increased in 2012, moving from 7.25% per year (1.33% in real terms) to 13.75% per year (7.02% in real terms) in December 2016. Since 2016, the basic interest rate has been reduced in nominal and real terms, as inflation rates were decreasing, following the low growth of the economy9.
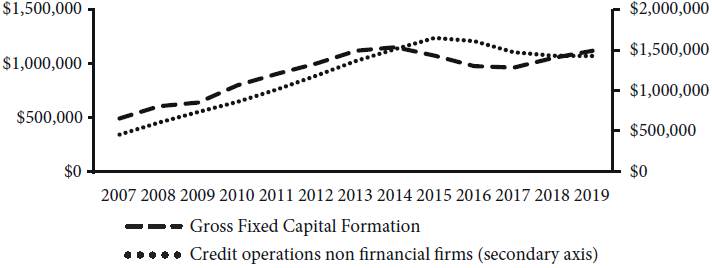
Source: Brazilian Statistical Office, Quarterly National Accounts, and the Brazilian Central Bank.
Figure 2 Gross Fixed Capital Formation and Non-Financial Firms Credit Operations (non earmarked credit) in nominal terms 2007-2019 (R$ Million)
It should also be considered that, in the case of Brazil, building up the financial fragility of non-financial firms along the investment cycle should take into account the very conservative way that monetary policy has been conducted in the 2000s and 2010s10. The conservative management has led to a very high level of nominal and real interest rates (one of the highest in the world) and a long period of appreciation of the nominal and real exchange rates.
To illustrate the behaviour of the real interest rate during the investment cycle in the 2000s and 2010s, Figure 3 displays the movement of ex-post short-term real interest rates since 1999, when the tripod of macroeconomic arrangement started been implemented. The dotted lines show the average real interest rate during the subperiods 1999-2009 (9.36% per year) and 2010-2019 (4.04 % per year). Despite the high level, the real interest rate has been showing a trend to decrease, the average that prevailed in both periods is very high compared with that which prevailed in developed and many other developing countries.
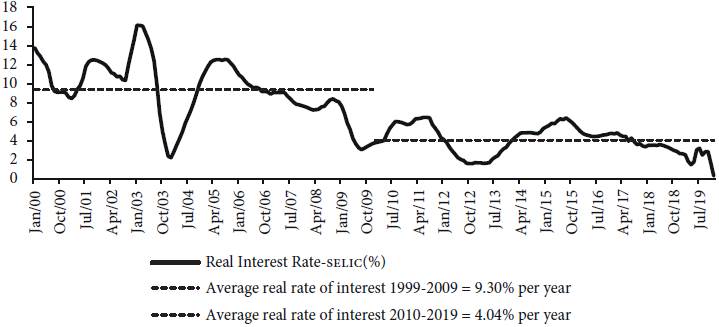
Source: Central Bank of Brazil for short-term nominal interest rates. Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) for consumer inflation rate (IPCA). Real interest rates (SELIC) calculated by the authors and deflated by IPCA.
Figure 3 Ex-post short-term real interest rates (%), 2000-2019
Therefore, in our interpretation, the 2008 international financial crisis and its long unfolding in the following years increased the financial fragility of firms as domestic macroeconomic scenario also deteriorated, either because of the increase in the domestic interest rate and also because of exchange rate depreciation. Actually, from 2013 to 2015 (the first year of the recession) the real exchange rate depreciated by 24%. The economic measures taken in 2011 onwards to boost investment showed little efficacy, as mentioned by Serrano and Summa (2015), because they did not reverse business expectations (see, also, Arestis, Baltar, and Prates, 2016). The domestic macroeconomic indicators (public debt and inflation) were worse off, contributing to blurring the prospects of the economy. From 2014 on, the Brazilian economy entered a recessive phase.
4. THE FINANCIAL FRAGILITY INDEX OF THE INDUSTRIAL SECTOR ALONG THE INVESTMENT CYCLE
The financial fragility hypothesis states that the economy will turn more fragile, the faster the number of firms with difficulties to roll over past debt commitments grows. In this section we will propose an aggregate index proxy of financial fragility for the industrial firms, based on the composition of receipts and costs and expenditures, inspired in Minsky’s definition of gross income. To contribute to the understanding of the investment cycle of the Brazilian economy in the 2000s and 2010s, we will present an econometric exercise to explain the determinants of an aggregate index of sectorial financial fragility (i) of industrial firms during the 2007-2016 period (t). The index is built based on the 25 sectors of activity from the Annual Industrial Survey11. Data are available at sectors of activity, therefore our empirical analysis will consider the aggregation of sectors of activity, and not individual firms12.
Figure 4 shows the evolution of the aggregate index of the financial fragility for industrial firms (manufacturing and mining). We built this index inspired by Minsky’s definition of the amount of cash that firms dispose to face duties and debt commitments to keep the business running in relation to their contractual commitments. In our case, the amount of cash should consider not only the gross-profit as obtained by the running of the business, but also non-operational receipts. Minsky (1986, p. 200) defines the operational receipts as quasi-rents. Besides the flow of quasi-rents, Minsky considers that firms should also be able to contract new debts and roll over old ones when needed to keep business running. In order to be able to do so, they should keep liquid assets in their portfolio. Therefore, the proxy of the aggregate financial fragility index (f) for the industrial firms is built as follows:
Where rit is the total receipts (which includes operational and non-operational receipts), cit is the total costs and expenditures (operational costs and non-operational costs) and (tit + dit + noeit ) are respectively taxes and duties (tit ), depreciation (dit ) and other non-operational expenditures (noeit ).
As defined, the aggregate index proxy of the financial fragility of the industrial firms considers the sensitivity of the industrial firm to the negative impact due to the divergence between the cash flow and debt commitments. Thus, a drop in the value of this index suggests a reduction in the payment capacity in relation to past contractual commitments, increasing firm’s fragility. Given the mathematical construction of the index, we opted to use it in an inverse form, so the mathematical manipulation guarantees the literal interpretation of the index in terms of increasing and reducing financial fragility ((fit )-1).
Figure 4 displays the evolution of the indicator proxy of financial fragility of the industrial sector. From 2010 onwards, financial fragility increases, reaching the highest level in 2015, meaning that the industrial surplus had been falling due to increasing weight of debt commitments13.
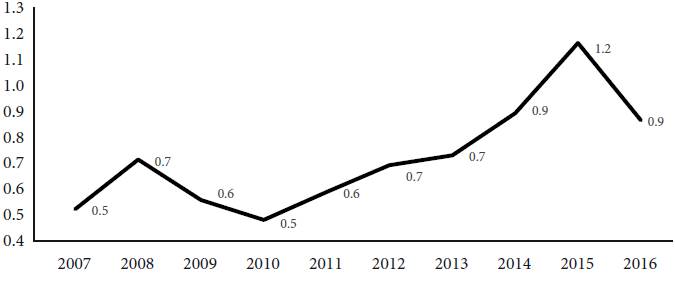
Source: Brazilian Statistical Office, Annual Industrial Survey (own elaboration).
Figure 4 Indicator proxy of the aggregate financial fragility of the manufacturing and mining industries, 2006-2016
To further expand the analogy with Minsky’s financial fragility typology, Figure 5 exhibits the distribution of the number of industrial sectors in hedge, speculative and Ponzi. We adopted the following ad hoc criteria to classify the sectors14: Hedge when the average financial fragility index of the sector was equal or below 0.5; Ponzi when the financial fragility index was equal or more than 0.9 and speculative sectors when the index was above 0.5 and below 0.9. The results in Figure 5 confirm our interpretation that the financial fragility of the industrial sector intensified in the 2010s mainly due to changes in the domestic economic policy and also to the slow recovery of the world economy. From 2013 to 2015 the number of sectors classified in a Ponzi position moved from 4 in 2013 to 11 in 2014 and 17 (more than 50% of the sectors) in 2015.
5. AN ECONOMETRIC EXERCISE TO EXPLAIN AGGREGATE FINANCIAL FRAGILITY IN THE INDUSTRIAL SECTOR, 2007-2016
In order to estimate the econometric equation for aggregate financial fragility, we assume the following hypotheses: i) The more the firm resorts to financing fixed asset expenditures to third party resources via credit, the more it exposes its balance sheet to market vicissitudes; ii) an increase in the interest rate increases the indebtedness over time and aggravates the firm’s financial fragility; iii) once installed, financial fragility has properties of persistence over time, as past debt commitments have to be honoured with present cash flow and/or more credit.
Our estimation strategy takes into account the possible simultaneous relationship of financial fragility with the choices of accumulating fixed assets and financial assets. The vulnerable situation of the non-financial firm to macroeconomic events may not yet be perfectly captured by the proxies of the estimated model. For this reason, the Arellano-Bond and Arellano-Bover estimators are used to address possible problems associated with specification, simultaneity or measurement error (Arellano and Bond, 1991; Windmeijer, 2005; Arellano and Bover, 1995; Blundell and Bond, 1998). In addition to the dynamic panel estimators, a static model with a fixed effect is estimated, controlling for non-observed sectoral heterogeneity invariant over time.
We use two set of variables to explain the behavior of the aggregate financial fragility proxy (f)-1: A sectoral vector and a macroeconomic vector. In the first case the variables are: The investment rate in gross fixed capital formation (I), the share of wages in the value-added (S) and the financial income as a share of financial revenues in total revenue (R). The macroeconomic variables are Credit outstanding in relation to the investment flow in fixed assets (D) and the basic interest rate (J). In formal terms we can write [1], where a1 is the constant term:
The expected sign of the investment rate (I) is positive as the increase in capital immobilization implies a greater commitment of current resources to the payment of contracts assumed in the present and in the past, increasing the financial fragility. The increase in the share of wages in the value added (S) should also show a positive sign, as it is an indicative of the increase in production costs that reduces the availability of internal resources to meet past commitments. The sign of the share of financial revenue in total revenue (R) may be ambiguous. If positive, it signals that operating revenues are decreasing and, thus, increasing the financial fragility of the balance sheets. If negative, it can signal that firms are adopting defensive positions and increasing their cash flow with financial income. The expected signal of the next both the variables - balance of credit operations in relation to capital fixed assets (D) and the interest rates (J) -is positive as the greater use of third-party resources increase the exposure of firms to variations in either the supply or the cost of credit.
Taking the natural logarithm (ln) on both sides of equation [1] of the model, assuming a random error uit , we arrive at the equation to be estimated with the panel data. The heterogeneity of the industrial sectors is determined by individual characteristics that do not vary over time ( i ; the neglect of this aspect in a piled estimation can generate an endogeneity problem caused by an omitted variable.
As before, the subscript (i) stands for sectors of activity and the subscritpt (t) for year15.
Based on equation [2], three estimators are used to minimize possible sources of endogeneity on the determinants of financial fragility: The static data estimator in panel with fixed effect (fe) and the dynamic estimators Arellano-Bond and Arellano-Bover. The static estimator deals with problems of omitted variables but is biased to determine the temporal persistence of financial fragility. The dynamic estimators Arellano-Bond and Arellano-Bover are more appropriate in the presence of temporal persistence of the dependent variable.
The Arellano-Bond estimator is called generalized moment in differences (gmm-Dif),
the dynamic nature of the difference estimator eliminates sectoral heterogeneity and
verifies the temporal persistence of fragility. The gmm-Dif treats the other sources
of endogeneity subject to the hypothesis of sequentially exogenous independent
variables
The Arellano-Bover dynamic estimator, called Systemic gmm (gmm-Sys), is an extension
of gmm-Dif. This estimator explores the additional premise of non-correlation
between the independent variables and the sectoral heterogeneity
Table 2 shows the results of unit root tests on the intercept and trend of the variables of the model. All tests show that the variables are non-stationary in level and stationary in the first difference. According to most tests, the variables are integrated in order of [I(1)], at 1% significance. The order of integration of the variables is essential to understand the coevolution of the studied phenomenon or the spurious nature of an allegedly biased equation.
Table 2 Unit root test of the model in individual linear trends
| Variable | Levin, Lin and Chu | Breitung | Im, Pesaran and Shin | ADF-Fisher | PP-Fisher |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnfit | -15.8975*** | -2.89997*** | -3.44367*** | 140.704*** | 291.357*** |
| lnRit | -16.7896*** | -3.9978*** | -3.34873*** | 133.945*** | 201.503*** |
| lnIit | -23.3813*** | -1.9343** | -2.98652*** | 120.522*** | 186.024*** |
| lnSit | -24.3236*** | -3.59372*** | -5.87482*** | 166.235*** | 269.753*** |
| lnJit | -14.1987*** | -15.6464*** | -1.36232* | 86.8633*** | 182.245*** |
| lnDit | -20.3787*** | -2.11551** | -2.99984*** | 135.025*** | 172.759*** |
Automatic selection of maximum lags based on MAIC: 0 to 9 with Newey-West fixed bandwidth and Bartlett kernel; ** Probabilities for Fisher tests are computed using an asymptotic Chi-quare distribution. All other tests assume asymptotic normality.
Tests Levin, Lin and Chu t, Breitung t; Im, Pesaran and Shin w; Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF)-Fisher χ2; Phillips-Perron (pp)-Fisher χ2: Ho: Panels contain unit roots or all panels contain unit roots; Ha: Panels are stationary or Some panels are stationary.
The stability of the estimated parameters of a temporal equation depends on the long-term equilibrium of the estimated model. This balance is determined by the Pedroni cointegration test, originally built to analyze the stability of data panels with long time. One of the conditions for carrying out the test is that the variables have the same order of integration, as seen in Table 2. If the absence of cointegration or divergences in the order of integration of the variables was verified, the equation could be spurious. However, given the results of Table 2, the Pedroni test (Pedroni, 1999, 2004) in Table 3, rejects the null hypotheses of absence of cointegration in favor of the alternative hypotheses of cointegrated panel at 1% significance.
Table 3 Pedroni cointegration test
| Tests | Lags max | Panel a | Panel b |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADF | 1 | -9.4553*** | -1.7762** |
| 2 | -6.055e+15*** | -20.2407*** | |
| MVR | 1 to 2 | -8.7347*** | |
| pp | -6.6743*** | -3.9639*** | |
| ppm | 7.8986*** | 5.4470*** |
Notes: Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF); Modified variance ratio (MVR); Phillips-Perron (PP); Modified Phillips-Perron (PPM).
Hypothesis Pedroni test: Ho is no cointegration and Ha are all panels cointegrated.
a/ Alternative hypothesis: AR parameter (within dimension).
b/ Alternative hypothesis: AR parameter (between dimension).
*** Significance level: 1%.
Table 4 shows the result of the estimates of the model. The hypothesis that the financial fragility of industrial firms is affected as credit operations increase more than proportionally to the gross fixed capital expenditures of the economy is confirmed in the three empirical exercises at 1% of statistical significance. This disproportion can indicate the moment when the macroeconomic context begins to change negatively for those firms with a greater degree of dependence on third-party resources to maintain their contractual commitments, meaning that the financial fragility might be increasing. The static estimator suggests a positive inelastic effect of the increase in the credit balance relative to capital immobilization. However, the temporal persistence of the financial fragility suggests the presence of bias to the static estimator, leading us to accept that this elasticity over the industry’s sectoral fragility is greater than 1. The Sargan test does not reject the hypothesis of overidentification of the model, therefore we accept the alternative hypothesis that dynamic equations are identified, up to 10% of significance.
Table 4 Estimated model
| Variables | Fixed effect | GMM-Dif | GMM-Sys |
|---|---|---|---|
| ln((fit-1 )-1) | -0.293*** | -0.176** | |
| (-2.67) | (-1.98) | ||
| lnRit | -0.0635 | 0.0494 | 0.154** |
| (-1.48) | (-0.8) | (-2.22) | |
| lnIit | 0.123* | 0.0274 | 0.246*** |
| (-2.00) | (-0.54) | (-2.75) | |
| lnSit | 1.026*** | 0.650*** | 0.247 |
| (-7.27) | (-3.78) | (-0.94) | |
| lnJt | 0.531*** | 0.441*** | 0.325 |
| (-7.92) | (-5.37) | (-1.03) | |
| lnDt | 0.650*** | 1.088*** | 1.219*** |
| (-3.71) | (-2.73) | (-2.85) | |
| Constant | -3.870*** | -6.172** | -6.065*** |
| (-3.69) | (-3.13) | (-2.94) | |
| Number observations | 247 | 194 | 222 |
| Number of groups | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Chow test | 9.06*** | ||
| Hausman test | 189.64*** | ||
| F test | 55.86*** | ||
| Wald test | 171.87*** | 195.81*** | |
| Instruments | 27 | 43 | |
| Sargan test | 23.84159 | 22.95418 | |
| Abond test (AR1) | -1.8452* | -2.6867*** | |
| Abond test (AR2) | -0.7224 | 0.64118 |
Note: *** significance at 1%, ** at 5%, * at 10%; in bracktes are the estimates for the standard deviation robust of the estimated coefficients.
Source: Authors own elaboration.
The hypothesis of temporal persistence of financial fragility is clearly identified in dynamic generalized moment estimators (GMM). This result is confirmed by the first-order serial autocorrelation Abond test. This test rejects the hypothesis of the absence of a first order serial correlation at 1% and does not reject the hypothesis of second order serial autocorrelation. First-order autocorrelation is captured by the parameter of the lagged fragility variable (Barros et al., 2020). The negative sign of the lagged fragility coefficient suggests that the autoregressive effect of the financial fragility index is decreasing, this means that everything constant, it tends to disappear over time.
The GMM-Dif estimator is identified according to the Sargan test and autocorrelated of the first order, as shown by the Abond test and the time persistence coefficient of fragility ln((fit-1 )-1). In it, the variables of interest rate level and the share of wages in value-added, as well as in the fixed effect estimator, are positively associated with financial fragility at 1% significance. This confirms the hypothesis that an increase in interest rates positively impact the indicator of financial fragility as it reduces firms’ cash availability to meet their contractual commitments, as well as wage costs.
Finally, the variables share of financial income over total income (R) and investment rate (I) are significant in the gmm-Sys estimator. Both elasticities are much less expressive than that of the macroeconomic variable (D), but they are also associated with current financial fragility16.
The coevolution between the disproportion of the balance of credit operations in relation to investment in the economy, the rate of investment in industry and the increase in the importance of the financial revenue of industrial firms in relation to the total revenue generated by them is an important result of the econometric exercise which qualifies the slowdown in the growth of the Brazilian economy in the years 2010s. Since the economy was in an ascending phase of the investment cycle, the change in economic policy, captured in the model by the credit/investment ratio and the importance of the interest rate, negatively impacted the industrial firm’s cash generation to honor contractual commitments. Moreover, from the firms’ point of view, the increase in wage share reduced the generation of internal funds.
CONCLUDING REMARKS
Our conclusion is that the Brazilian economy was in the ascending phase of an investment cycle when external conditions changed due to the 2008 international financial crisis. The new government that took office in 2011 changed the way macroeconomic policy had been conducted since 1999, shifting macroeconomic policies from the incentive to aggregate demand to supply-side incentives. The changes did not improve the macroeconomic context, inflation rates accelerated, government savings became negative and current deficits increased. In the most deteriorated international and domestic scenarios, the investment cycle enters a descending phase and the indicator for the financial fragility of the industrial firms showed that the capacity of generating cash flow to meet contractual commitments worse off.
In our econometric exercise to explain industrial firms’ financial fragility determinants, we separate the variables in two sets: One capturing sectoral movements and other capturing macroeconomic movements. The first one captured the industrial firms’ capacity to generate cash-flow to meet contractual commitments and the second one the macroeconomic conditions for financing the investment along the cycle. The econometric model successfully showed the coevolution of industrial firms’ financial fragility and the deterioration of the macroeconomic context, via credit decoupling to sustain investment in fixed capital and the shock in the interest rate in the first half of the 2010s. In this sense, this paper sheds new light to explain the reasons why the Brazilian economy has dove into a recession since 2015. The investment rate of non-financial firms, particularly those in the industrial sector, does not resume given that economic prospects are still blurred. The fiscal austerity implemented since 2015 and the liberal reforms since 2016 did not deliver growth and the Brazilian economy is stagnating.











 nueva página del texto (beta)
nueva página del texto (beta)



