Introduction
Total fish production from capture fisheries and aquaculture is estimated to reach 172 million tons in 2021; aquaculture production is expected to exceed capture fisheries production and to increase around 33% because of higher demand for fish consumption (FAO, 2012). Thus, the establishment of a balance between high production, low cost and quality comes into prominence in aquaculture. Successful production mainly depends on broodstock management, larval husbandry and nutritional quality of feed in larval and juvenile feeding period (Izquierdo et al., 2001; Infante & Cahu, 2010).
Fishmeal and fish oil are the main two components of marine fish feeds, from which protein and lipids are obtained respectively. Fish oil is the major source of n-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 LC-PUFA), such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; 22:6n-3) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; 20:5n-3), that are crucial for cultured fish and for the aqua feed industry (Tacon & Metian, 2008; Turchini et al., 2009). However, price of fish oil-based products is rising due to its increased demand and limited production. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain alternative sources in order to assure sustainable aquaculture production (Izquierdo, 2005).
Terrestrial plant oils such as sunflower, soybean, canola, rapeseed, palm, cottonsed and linseed oils, have been evaluated as replacement of fish oil for several fish species (Bell et al., 2003; Bransden et al., 2003; Huang et al., 2007; Piedecausa et al., 2007; Fountoulaki et al., 2009; Bell et al., 2010; Eroldoğan et al., 2012). Except salmonids, most marine fish are not capable of synthesizing n-3 LC-PUFA because of their limited delta 5 and delta 6 desaturase enzymes expression by their genes (Sargent et al., 2002). Since complete or partial replacement of fish oil by vegetable oils can reduce the essential n-3 LC-PUFA level of fish fed with these diets (Bell et al., 2003; Bell et al., 2004; Torstensen et al., 2005; Mourente & Bell, 2006) and could negatively affect health and flesh quality of gilthead sea bream (Montero et al., 2003; Izquierdo, 2005; Cruz-Garcia et al., 2011), n-3 LC-PUFA should be present in marine fish diets in order to support high levels of n-3 LC-PUFA in fish.
Marine microalgae are the primary producers of n-3 LC-PUFA in the aquatic food chain, and are commonly used in aquaculture as a source of essential nutrients such as n-3 LC-PUFA, vitamins and pigments to feed molluscs, crustaceans, rotifers and Artemia (Muller-Feuga, 2000). More recently, much interest has been paid to the industrial production of microalgae for biofuel and for the nutraceutical market. Many studies have been focused on the production of alternative sources of n-3 LC-PUFA from microalgae (Ratledge, 2001; de Swaaf, 2003; Ganuza & Izquierdo, 2007) and single cell biomass of some species is now commercially available as a free flowing powder that could easily be used as aquafeed ingredient.
Some studies succeeded to use those microalgae based n-3 LC-PUFA sources as an alternative to fish oil (Atalah et al., 2007; Miller et al., 2007; Ganuza et al., 2008; Eryalçın et al., 2013). While production costs for single cell LC-PUFA is still not competitive with current fish oil prices (Pulz & Gross, 2004; Spolaore et al., 2006), development of microalgae for biodiesel and food industry could bring their cost to a level that might eventually compete with the raising fish oil prices.
Nannochloropsis gaditana L. M. Lubián 1982 is a phototrophic eustigmatophyte widely used in larval rearing, especially for rotifer production and for larval rearing with the greenwater technique. N. gaditana is rich in eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; 20:5n-3) and during rotifer enrichment provides high levels of EPA and protein (Sukenik, 1991; Rocha et al., 2003; Ferreira et al., 2009). Crypthecodinium cohnii (Seligo) Javornicky, 1962 is a heterotrophic dinoflagellate rich in docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; 22:6n-3) and it is used as a source of this fatty acid in several aquaculture applications (Barclay et al., 1994; Kyle, 1996; Apt & Behrens, 1999; Ganuza & Izquierdo 2007; Ganuza et al., 2008; Eryalçın et al., 2013). It can produce high amounts of DHA (close to 10% dry weight or 40% total fatty acids of its biomass) and is low in other short chain fatty acids (Kyle & Gladue, 1991; Kyle et al., 1992; Sijtsma & de Swaaf, 2004; Ganuza & Izquierdo, 2007).
It was shown that microalgae biomass could be used as DHA sources alternative to fish oil in microdiets for gilthead seabream larvae (Vazhappilly & Chen, 1998; de Swaaf et al., 1999; Ganuza & Izquierdo, 2007; Eryalçın et al., 2013), and that their inclusion of commercial EPA sources in gilthead seabream weaning diets resulted in high total length and in survival rates similar to those obtained with diets containing different microalgae products (Eryalçın et al., 2013). C. cohnii was successfully used to substitute fish oil DHA in gilthead seabream weaning diets (Ganuza et al., 2008), but the necessity for EPA sources was highlighted by the authors. When DHA requirements are fulfilled by the diet, EPA unbalance may affect growth, survival and resistance to stress (Liu et al., 2002; Izquierdo & Koven, 2011; Eryalçın et al., 2013). Nannochloropsis species are commonly used in greenwater for larvae cultures as a source of EPA and their beneficial effects are well known for Sparidae species, but they are rarely used as a feed ingredient.
The aim of this study was to investigate whether DHA and EPA from fish oil sources could be replaced by freshly cultured lyophilized microalgae C. cohnii and N. gaditana. In order to evaluate the effects of the microalgae oils, growth performance, survival, digestive morphology and fatty acid compositions of the gilthead sea bream larvae were studied.
Material and methods
Microalgae culture. N. gaditana was cultured phototrophically in 300-L plastic bags using F/2 medium (Guillard & Ryther, 1962). The bags were operated in a batch mode at 25 °C, 5 vol air/vol culture min and 400 µM photon/m2/s. C. cohnii ATCC 50060 was produced heterotrophically in a 10-L fermenter (Bioflo 3000, New Brunswick) using a seawater medium with ethanol and yeast extract as sole ingredients. The fermenters were operated on a fed batch mode according to the protocol described by de Swaaf et al. (2003). Both algal biomasses were harvested at the stationary phase of the culture by centrifugation (3000 g, 5 min, 10 °C). The biomass was washed twice with demineralized water at 3 °C in order to eliminate the residual salts.
Fish husbandry. Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata Linnaeus, 1758) larvae were obtained from natural spawnings from Instituto Canario de Ciencias Marinas [Grupo de Investigación en Acuicultura (GIA), Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain]. Larvae (5.97±0.4 mm total length, mean ± SD; 0.012 ± 0.001 mg dry body weight) previously fed rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis Müller, 1786) enriched with DHA Protein Selco(r) (INVE, Dendermond, Belgium) until 20 days after hatching (dah) were randomly distributed in 12 light grey fiberglass cylinder tanks (200-L) at a density of 2100 larvae tank-1 and fed one of the diets tested in triplicate. All tanks were supplied with filtered seawater (37 g L-1 salinity) at a rate of 0.4 L min-1 during the first week, which was increased to 1.0 L min-1 during the second week of the experiment. Water entered from the tank bottom and exited from the top to ensure water renewal and maintain high water quality. Ammonia and nitrite were measured twice a week (Marine and Fresh-water Test Lab, Red Sea Europe, Verneuil sur Avre, France) during the experiment. Values were always below detectable levels for ammonia (NH4+ <0.2 mg/L) and nitrite (NO2- <0.02 mg/L). Water was continuously aerated (125 ml min-1) attaining 6.2±0.5 mg L-1 dissolved O2. Mean water temperature and pH throughout the trial were 18.3±0.2 °C and 7.75, respectively. Photoperiod was kept at 12 h light/12 h dark, by white daylight fluorescent tubes, and light intensity was kept at 1,700 lux (digital Lux Tester YF-1065, Powertech Rentals, Osborne Park City, WA, Australia).
Experimental diets. Four experimental microdiets (pellet size <250 µm) with different sources of EPA and DHA were prepared (Table 1): a control diet (Control) based on fish oil (Capelin oil, Norsildmel, Bergen, Norway) and squid powder (Rieber & Son, Bergen, Norway) as lipid and protein sources; a diet containing 11% Nannochloropsis gaditana (diet N) to substitute completely fish oil and replace squid meal partially; a diet containing 8% Crypthecodinium cohnii (diet C) to substitute completely capelin oil and replace partially squid meal; a diet containing equal amounts of 5.5 % Nannochloropsis gaditana and Crypthecodinium cohnii (diet N+C) substituting squid powder and capelin oil. The squid powder in diet N+C was lowered in order to balance the protein added as microalgae. Consequently, the lowered EFA content was balanced with 5.5% fish oil. The desired lipid content of experimental diets was adjusted with a non-essential fatty acid source, oleic acid (1.5 %). The total lipid content of the different diets ranged between13 and 17% dry weight. The ingredients were mixed in a mortar and then combined with gelatin dissolved in water at 80 °C. The feed paste obtained was compressed, pelleted and dried in an oven at 40 °C for 24 h. The pellets were ground in a Sample Mill (Braun KSM 2) and sieved to obtain a particle size of 150-250 µm (Atalah et al., 2012; Eryalçın et al., 2013).
Table 1: Formulation and proximate composition of experimental diets. From species.
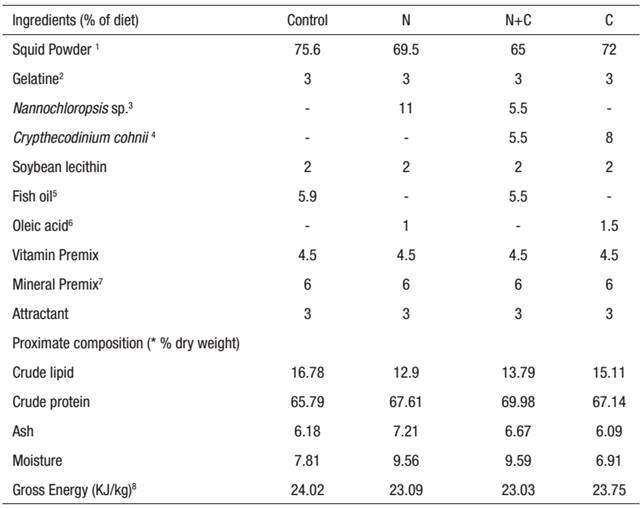
1 Squid meal (Riber & Son. Bergen, Norway). 2 Gelatine 80-100 Blooms, Pancreac, Espana. 3 Lyophilized N.gaditana biomass. 4 Lyophilized Crypthecodinium biomass. 5 Fish oil (Capelin oil, Denofa, Fredrikstad, Norway). 6 Oleic acid Vegetable, Merch, Darmstadt, Germany. 7 Teshima, Kanazawa and Sakamoto (1982). 8Microdiet gross energy content was estimated as: total carbonhydrate x 17.2 J/kg; fat x 39.5 J/kg; protein x 23.5 J/kg. * Mean values (n=3) are quoted in order to include the analytical error.
No microalgae were added to the experimental tanks during the feeding trial. Larvae were fed by hand with the experimental diets for 17 days every 45 min during light periods. The first four days of the experiment, larvae were fed with non-enriched rotifers twice a day at 12:00 and 16:00 hours to maintain a rotifer density of 2 ind. mL-1 in rearing tanks. During the first week feeding rate was 2 g per day, which was adjusted to 2.5 g per day during the second week. Larvae were observed under microscope to determine feed acceptance. The tanks were siphoned daily in order to collect uneaten food and feces.
Growth performance. Larval growth was determined measuring total length of 30 larvae 20, 27 and 34 dah using a profile projector (Mitutoyo Profile Projector PJ-A3000). Survival rate was determined counting all live larvae at the end of the experiment. Air exposure stress resistance test was applied to 25 larvae of each tank. For that purpose, larvae were held out of the water for 1 min 30 sec in a scoop net and then subsequently moved into 2-L beaker with aerated water. Survival was determined after 24 h by counting dead larvae. At the end of the feeding trial, microdiets and all larvae in tanks were collected and stored at -80 °C in plastic bags until proximate composition was carried out. Moisture, total protein and ash content were determined drying for 24 h at 105 °C, as total Kjeldahl nitrogen and after incinerating the dried samples at 600 °C for 24 h, respectively (A.O.A.C. 2005). Total lipid contents of larvae and microdiets were determined gravimetrically after extraction with chloroform-methanol (2:1) (Folch et al. 1957).
Ingestion of all experimental diets was checked by microphotography of larval digestive system after 7 days of feeding. If apparent feed intake differences were observed, diet acceptance was determined observing the abdominal cavity of 30 larvae of each tank with a stereoscope (Leica Wild M3Z, Optotek, California, USA), and measuring the area of the gut occupied by digested matter on the micrographs, using Image Pro Plus(r) (Media Cybernetics Inc., Silver Springs, MD, USA) semiautomatic image analysis system.
Fatty acid methyl esters preparation and quantification. Fatty acid methyl esters in microalgae, diets and experimental fish were obtained by transmethylation with 1% sulphuric acid in methanol (Christie, 1982). Fatty acid methyl esters were separated by GC (GC-14A; Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan) in a Supercolvax-10- fused silica capillary column (constant pressure with 100KPa, length: 30 m; internal diameter: 0.32 mm; 0,25 i.d (Ref.:24080-U) Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA) using helium as a carrier gas. Column temperature was 180 °C for the first 10 min, increasing to 220 °C at a rate of 2 °C min-1 and then held at 220 °C for 15 min. Fatty acid methyl esters were quantified by FID following the conditions described in Izquierdo et al. (1990) and identified by comparison with external standards and well characterized fish oils (EPA 28, Nippai, Ltd Tokyo, Japan). Fatty acid profiles of microalgae and experimental diets are shown in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively.
Table 2: Fatty acid composition of microalgae (* % of total lipid).
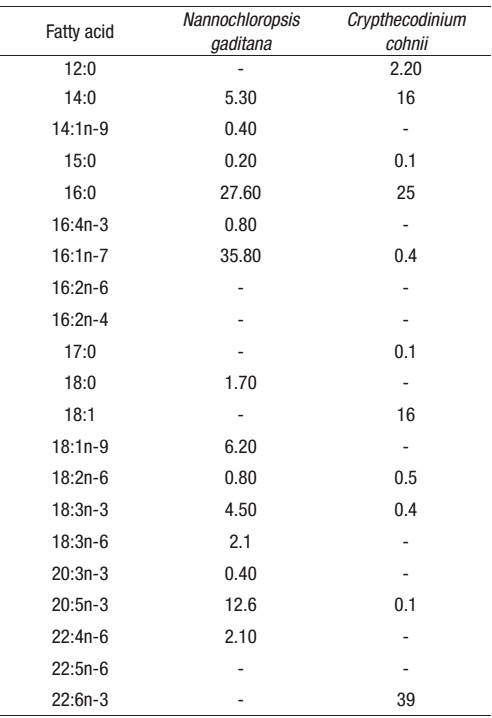
* Mean values (n=3) are quoted in order to include the analytical error.
Table 3: Fatty acid composition of the experimental diets (* % dry weight, n=3).
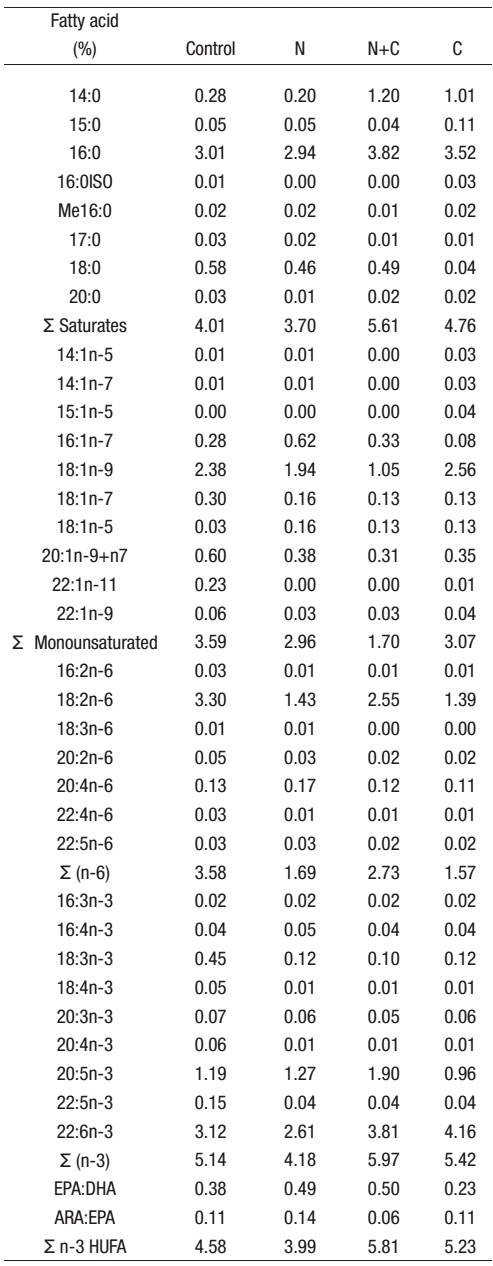
* Mean values (n=3) are quoted in order to include the analytical error.
Statistical analysis. All data were normal and homoscedastic (Shapiro-Wilk's test was used for normality and Levene's tests), not requiring any transformation and were treated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Means were compared by Tukey tests (p < 0.05) using SPSS software (SPSS for Windows 11.5; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Final survival rates were not statistically different (34%-69%, average) (p > 0.05) (Fig. 3). Similarly, air exposure stress resistance survival results were similar among the groups fed with different experimental diets. After 7 days of experimental feeding (27dah), larvae fed diet C had a significantly (p < 0.05) higher total length than larvae fed diets containing N. gaditana (diet N and N+C), but differences in weight were not significant. At the end of the experiment, larvae fed either control or C diet had significantly (p < 0.05) higher total length and dry weight than larvae fed N and N+C diets, which were not significantly different (Fig. 1-Fig. 2).
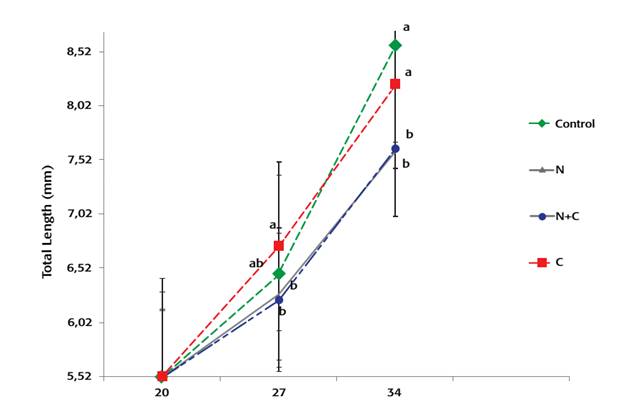
Figure 1: Total lenght of gilthead sea bream larvae fed experimental diets. Treatments containing different letters each datapoint were significantly different (p < 0.05).
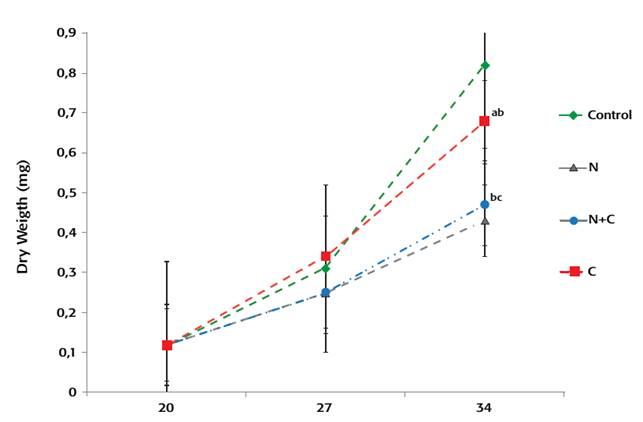
Figure 2: Dry weight of gilthead sea bream larvae fed with expermental diets Treatments containing different leters in each datapoint were significantly different (p < 0.05).
At the end of the study, larvae fed the Control and C diets showed higher protein level than other groups, and lipids were higher in control group larvae than in C and N groups. The moisture content was higher in the control group in comparison to other groups, while the group with highest ash content was the N group (Table 4).
Table 4: Proximate composition of experimental larvae fed diets containing different microalgae for 14 days (* % of dry weight)
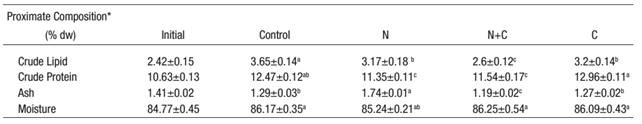
* Mean values (n=3) are quoted in order to include the analytical error.
Fatty acid analysis of experimental fish (% dry body weight) revealed that all the experimental diets caused an increase in saturated fatty acids content, mainly 16:0, in comparison to larvae fed the control diet. Total monounsaturated fatty acid levels were significantly (p <0 .05) lower in larvae fed with N, N+C and C diets compared to control group larvae (Table 5). Linolenic (18:3n-3) and linoleic (18:2n-6) acid levels of larvae fed with control diet were significantly (p < 0.05) higher than those of the other experimental groups. Total n-3 and n-6 fatty acid content of larvae fed with N, N+C and C diet was lower than in the control group (p < 0.05). Additionally, the total n-3 HUFA contents of larvae fed with Control and C diets were higher than those of larvae fed with diet N+C and N diet.
Table 5: Fatty acid composition of experimental larvae (* % dry weight, n=3).
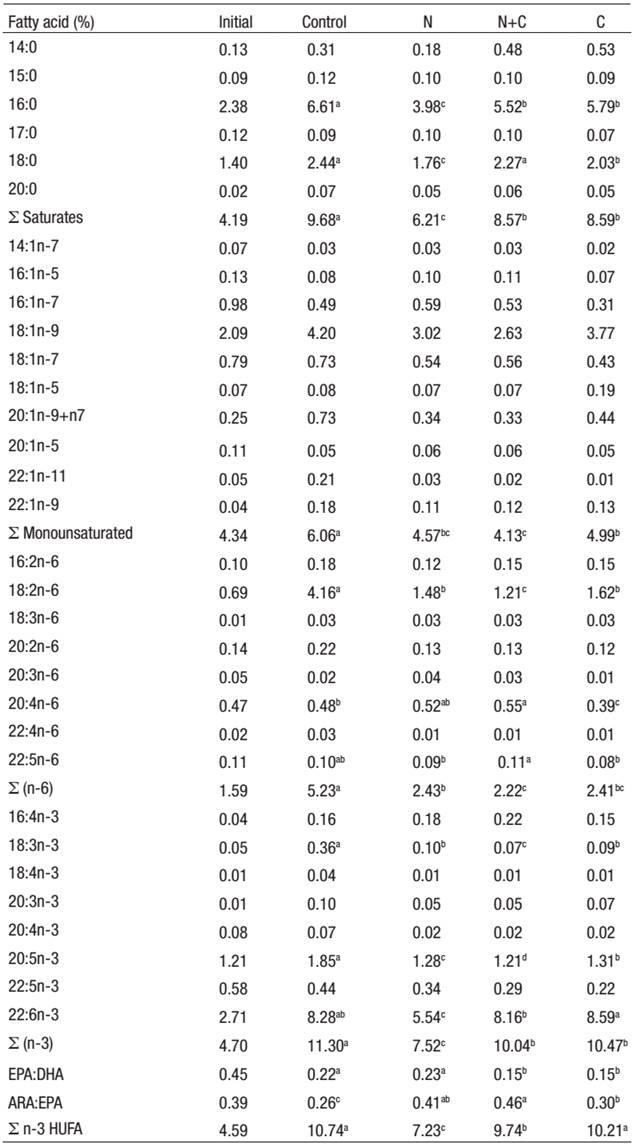
* Mean values (n=3) are quoted in order to include the analytical error.
Higher DHA (22:6n-3) accumulation was observed in larvae of C and Control groups. Additionally, EPA (20:5n-3) level was significantly higher in larvae fed with theControl diet. On the other hand, ARA (20:4n-6) level was found higher in larvae fed diets N+C and N than in those fed with Control and C diets. This result also reflected the ARA:EPA proportion of larvae. Larvae fed control diet and N diet showed higher EPA:DHA ratio due to the EPA rich in N. gaditana. On the other hand, fish fed diets N+C and C also showed very good levels of DHA.
Discussion
Fatty acid analysis confirmed that microalgae were effectively used as essential fatty acid sources in microdiets. Total n-3 LC-PUFA content of the larvae was improved with the inclusion of N. gaditana and C. cohnii as substitution to fish oil.
Survival and stress resistance of fish are important parameters to ensure good quality fish production. Survival of larvae depends mainly on nutritional quality of feeds and nursery conditions, and a large range of survival rates were obtained in various dietary experiments (e.g. Robin & Vincent, 2003; Ganuza et al., 2008; Eryalçın et al., 2013). In this study, larval survival rates ranged from 34 to 69% from 20-34 dah larvae, in agreement with these previous studies. The importance of EPA content in larval diet due to its critical effect on growth and survival was previously suggested by Ganuza et al. (2008) who concluded that DHA rich single cell microorganisms in microdiets can not replace completely fish based products. This requirement of EPA sources in microdiets for gilthead seabream larvae was also shown in other studies (Atalah et al., 2007; Eryalçın et al., 2013). It was suggested that the EPA:DHA ratio in marine fish larvae should be in the range 0.67 to 2.0 (Rodríguez et al., 1997; Atalah et al., 2007). In our diets with single cell sources, the EPA:DHA ratio varied from 0.23 to 0.50, which seems adequate for early development. In this study, DHA rich C. cohnii diet resulted in high growth rates, while the EPA rich N. gaditana diet led to mediocre growth. On the other hand N. gaditana and N+C diets gave higher ARA amount which is important for the immune system. Therefore, high growth rates and good survival could be expected from the combined diet containing both microalgae (N+C) but the obtained growth rates were not satisfactory. The combination of microalgae strains that can provide a wider range of fatty acids to obtain better dietary quality than single algae was previously suggested by Harel et al. (2002). According to our results, the combined use of C. cohnii and N. gaditana sustained survival rates, but was not sufficient to support high growth rates.
Dietary energy content is also important for the microdiet nutritional value. Lower amounts of accessible energy to larvae was previously suggested as a reason for total length differences observed at day 14 (Ronnestad et al., 1994). In the present study, N. gaditana and N+C diet had lower gross energy content compared to the fish oil diet or C. cohnii diet, which could be insufficient to cover the larvae's energy requirements during this fast growing phase. The N and C diets included oleic acid which is regarded as an important source of energy, during larval development of marine fish larvae (Van der Mereen et al., 1991). The oleic acid content might have supported the growth rates obtained from C diet, but does not seem sufficient for the low DHA containing N diet. The absence of oleic acid in the N+C diet on the other hand, might have led to low growth rates due to less available energy in diets.
Some microalgae species as N. gaditana are not only a good source of essential fatty acids, but also of pigments and vitamin E (Rebolloso-Fuentes et al., 2001; Durmaz, 2007; Hemaiswarya et al., 2011), which could be related to the good survival rates of larvae fed N. gaditana despite the lower DHA content in their body tissue. Vitamin E is an essential antioxidant synthesized by photosynthetic organisms (Durmaz, 2007) and its effect on growth, survival and resistance to stress are important along the whole life cycle in fish (Izquierdo et al., 2001; Montero et al. 2001; Vismara et al., 2003; Atalah et al., 2012).
In our study, single cell sources such as the dinoflagellate C. cohnii and eustigmatophyceae N. gaditana were effectively used as essential fatty acid sources in gilthead seabream larvae in comparison to the control group.
Particularly fish fed C. cohnii containing diet performed similar to fish fed the control diet containing fish oil. Diets with N. gaditana alone on the other hand could not effectively replace fish oil. N. gaditana could be used to complement possible EPA deficiencies for gilthead sea bream larvae but the combined use of the two microalgae C. cohnii and N. gaditana seem to necessitate additional energy source such as oleic acid. Future work should focus on longer experimental periods with weaning diets including different levels of these microorganisms in order to address the long-term effects on immune system and survival of gilthead sea bream larvae.











 nueva página del texto (beta)
nueva página del texto (beta)



