INTRODUCTION
Sargassum C. Agardh is a brown seaweed (Phaeophyceae) genus harboring at least 615 taxonomically accepted species, making it the most abundant genus within the Fucales order (Guiry & Guiry, 2022). Sargassum species are distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical zones of both hemispheres and often form dense underwater forests. These forests constitute key habitats that supply shelter to many species, such as fishes, invertebrates, and other algae. In the Gulf of California, Sargassum species are often dominant within communities due to their biomass (Suárez-Castillo et al., 2013). Sargassum species are of interest to study due to their capacity to synthesize secondary metabolites, including terpenoids, florotannins, polyphenols, volatile hydrocarbons, sulfated polysaccharides, and products of mixed biogenetic origin. As such, Sargassum species have unique chemical compositions, making them important sources of phycocolloids and compounds that may be used in fertilizers, fodder, food supplements, and compounds of pharmaceutical interest (Mascheck & Baker, 2008; Echavarría et al., 2009).
There are five Sargassum species that form underwater forests in the Gulf of California: S. johnstonii Setchell & N. L. Gardner; S. herporhizum, Setchell & N. L. Gardner; S. sinicola Setchell & N. L. Gardner; S. horridum Setchell & N. L. Gardner; and Slapazeanum Setchell & N. L. Gardner (Suárez-Castillo et al., 2013).
A few studies have been conducted with S. lapazeanum that have spanned a variety of topics including biogeography (Phillips, 1995), population dynamics (Rivera & Scrosati, 2006), taxonomy (Andrade-Sorcia et al., 2008; Norris, 2010), and biotechnology (Patrón-Prado et al., 2011). However, despite technological advances, no information is yet available for the biological activity of S. lapazeanum. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the potential of S. lapazeanum as a source of biologically active compounds, such as those with antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticoagulant activity. In addition, this study aimed to conduct a partial characterization of fucoidan active fractions and their structural nature.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sampling. Sargassum lapazeanum was collected by hand in the intertidal zone of the Tarabillas site (24°27’55.1” N, 110°41’20.1” W), which is located in La Paz, Baja California Sur, Mexico. Seaweed samples were collected at 1 m depth and transported to the laboratory in buckets at room temperature. In the laboratory, the seaweeds were thoroughly washed with tap water to remove epiphytes and sand and then sun-dried. After which, the seaweed samples were ground into particles (1 mm) and stored in plastic bags at room temperature until analysis.
Proximal analysis. A proximal analysis of the algal tissue was conducted at Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas del Noroeste (CIBNOR) in La Paz, Mexico, following the methods of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC, 2005). All analyses were conducted in triplicate. Moisture content was determined as the difference in sample weights before and after treatment at 110 °C for 4 h (AOAC 930.15). Ash content was determined as the difference in dry weight before and after calcination at 600 °C for 2 h (AOAC 942.05). Crude protein content was determined using a FP-528 Nitrogen/Protein Determinator (LECO, Saint Joseph, MI, USA) after determining the total nitrogen content and multiplying by a factor of 6.25 (AOAC 990.03). Crude lipid content was determined by direct extraction with diethyl ether using a Foss Tecator Soxtec Avanti 2050 Extraction System (FOSS Analytical, Höganäs, Sweden; AOAC 920.39). Crude fiber content was determined by the successive hydrolysis method (AOAC 978.10).
Ethanolic extract (EE). Three hundred grams of algae were extracted with ethanol (96%) at room temperature (25 °C) for one week, changing the solvent every other day. All obtained filtrates were combined into a final solution, which was concentrated to dryness with a RE500 rotary evaporator (Yamato, Orangeburg, NY, USA) at 40 °C. The obtained ethanolic extract (EE) was stored at -18 °C.
Ethanolic extract (EE) fractionation. Fifteen grams of EE was fractionated in a normal phase silica gel chromatography column using a mixture of the following solvents: CH2Cl2 100, CH2Cl2:EtOH 90:10, CH2Cl2:EtOH 25:75, CH2Cl2:EtOH 50:50, EtOH 100, EtOH:H2O 50:50 y H2O 100%. Seven fractions (F1-F7) were obtained. Subsequently, fraction F2 was selected for a second fractionation because it showed the highest antibacterial activity. This fraction was separated using the same chromatographic system with a mixture of the following solvents: CH2Cl2 100, CH2Cl2:MeOH 95:5, CH2Cl2:MeOH 90:10, CH2Cl2:MeOH 80:20, CH2Cl2:EtOH 70:30, CH2Cl2:MeOH 50:50, EtOH 100, and H2O 100%. Fourteen subfractions (FF1-FF14) were obtained as a result.
Crude fucoidan content and purification. Crude fucoidan (CF) was obtained following the method of Muñoz-Ochoa et al. (2009) with modifications. One hundred grams of algae were soaked in 600 mL of distilled water. The mixture was then placed in a water bath (Precision Scientific, Chicago, IL, USA) at 55 °C with continuous stirring for 2 h. The mixture was filtered, and the extract liquor was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 30 min (Beckman centrifuge TJ-6, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The clarified solution was decanted and precipitated with 40 mL of 10% calcium chloride to remove any soluble residual alginate, which was separated by centrifugation a 3000 rpm for 30 min. The clarified solution was precipitated with three volumes of ethanol. Then, the precipitate was separated by centrifugation for 15 min at 3000 rpm and dried at 50 °C.
The CF was dissolved in 150 mL of distilled water and partially purified by fractional precipitation with three volumes of ethanol, and the precipitate was recovered after each volume was added. The three precipitates (CFF1, CFF2, and CFF3) were obtained and dried at 55 °C for 24 h and stored at -18°C until analysis.
Antibacterial activity. This was evaluated in duplicate by the disc agar diffusion method of Kirby-Bauer (Bauer et al., 1966). For this study, Staphylococcus aureus Rosenbach 1884 (BAA-42); Escherichia coli Escherich1885 (BAA-196); Bacillus subtilis (Ehrenberg 1835) Cohn 1872; Vibrio harveyi Filippo Pacini 1854 (14126), and Vibrio parahaemolyticus Filippo Pacini 1854, were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and maintained in Mueller-Hinton media for marine bacteria (Mueller-Hinton 2.5% NaCl). Paper discs (6.5 mm diameter) impregnated with 2 mg of each sample (EE, F1−F7) were placed on plates of Mueller-Hinton agar that had been previously inoculated with a suspension of each test microorganism containing 1×108 cells mL−1. Inhibition zones were measured after 24 h of incubation at 37 °C. Ampicillin and erythromycin were used as positive controls, and solvents were used as negative controls.
Antioxidant activity. Free radical scavenging activity was evaluated using the bioautographic and colorimetric methods. For the former, the antioxidant constituents were analyzed using thin layer chromatography (TLC) following the methodology of Wang et al. (2012). Each sample (1 mg mL−1) was dissolved in the appropriate solvent, and 10 µL of each solution was loaded onto TLC plates. The plates were developed in a CH2Cl2:MeOH (9:1) system, sprayed with 0.2% DPPH solution in methanol, and left in the dark for 30 min at room temperature. After this time, antioxidant activity was detected by a change in color from purple to yellow, reflecting discoloration.
The colorimetric assay was conducted in duplicate following the method of Molyneux (2004). A stock solution of each sample [40 mg in 5 ml of EtOH:H2O (9:1)] was tested at different concentrations (400, 200, 100, 50, and 25 μg mL−1), and dose-effect curves were prepared. Each concentration (1 mL) was mixed with 4 mL of 0.02% DPPH solution in methanol and placed in the dark for 30 min at room temperature. The absorbance at 517 nm was measured in a spectrophotometer (Milton Roy, Spectronic 20D, Rochester, NY, USA). A blank was also prepared to obtain the color correction factor.
Free radical scavenging activity (SA) was calculated as the percentage of DPPH reduction using the formula:
where A0 is the blank absorbance and AS is the sample absorbance. With the data, a dose-effect curve was constructed by graphing the reduction percentage of DPPH regarding the concentration of the extract used. Further, the half effective concentration (EC50) values were calculated with a linear regression of the dose-effect curve. Ascorbic acid was used as a positive control.
Fucoidan anticoagulant activity. This was evaluated in duplicate according to instructions of the manufacturer (SIEMENS ®), by the increase in prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT). The PT and APTT were measured using human plasma treated with sodium citrate and a stock solution of 10 mg mL−1 of CF. The PT assay was carried out by mixing 90 µL of human plasma with 10 µL of stock solution followed by incubation at 37 °C for 1 min. After incubation, 200 µL of PT reagent (preincubated at the same temperature for 10 min) were added to the mixture. The APTT assay was carried out by mixing 90 µL of human plasma with 10 µL of stock solution and 100 µL of APTT reagent followed by incubation at 37 °C for 3 min. After incubation, 100 µL of 0.025 M CaCl2 (preincubated at the same temperature) were added to the mixture. The time for clot formation for PT and APTT was determined by visual inspection and recorded in seconds. Distilled water was used as a negative control while sodium heparin was used as a positive control in both assays.
Fucoidan Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) analysis. The CF as well as its fractions (CFF1, CFF2, and CFF3) were structurally characterized with an IR spectrophotometer (Perkin Elmer, TWO, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with an attenuator of total reflectance (ATR). Each spectrum was obtained by the addition of 14 scans (resolution of 4 cm−1) in the spectral range of 500-4000 cm−1. In addition, the sulfate content was calculated by the baseline method based on the sulphate/total sugars (SO4/CHOH) ratio determined from the area under the curve of the bands at 1250 and 1040 cm−1 (Lijour et al., 1994).
Alginate extraction. Sodium alginate was obtained in triplicate following the method of Rodríguez-Montesinos et al. (2008). Twenty grams of the algal residual obtained in the fucoidan process were hydrated overnight in 180 mL of 0.1% formaldehyde solution. The solution was drained, and the algal tissue was placed in 400 mL of distilled water. The pH was adjusted to 4 with 1N HCl and constant stirring for 15 min. The solution was drained, and the algal tissue was placed in 400 mL of distilled water. The pH was adjusted to 10 with 10% Na2CO3 in a water bath (80 °C) with constant stirring for 2 h. The resulting mixture was vacuum filtered using diatomaceous earth as a filter aid. The obtained solution was precipitated with one volume of ethanol (96%). The precipitate was then filtered, dried for 24 h at 55 °C, and stored at 4 °C. The alginate yield was computed as the percentage of algal dry weight.
Chemical properties of alginate. The viscosity of sodium alginate was measured in a 1% (w/v) alginate solution at 22 °C with a digital viscometer (Brookfield, DV-I, Middleboro, MA, USA) using the appropriate spindle. Alginate gel strength was measured using the 1% alginate solution. A dialysis membrane (2.9 cm diameter) was filled with the alginate solution and immersed overnight in 10% CaCl2. The gels were cut into three cylinders (2.9 cm diameter × 3 cm length), and gel strength was measured with a texture analyzer (Stable Micro Systems, TA.XT Plus, Godalming, Surrey, UK) (Borras-Chavez et al., 2016).
RESULTS
Proximal analysis. Sargassum lapazeanum is mainly composed of a high content of inorganic material and carbohydrates, corresponding to high values of nitrogen-free extract (NFE) and ash (Table 1). The lowest value recorded was that of the ether extract content.
Table 1 Composition of Sargassum lapazeanum from Tarabillas, Baja California Sur, Mexico. Mean ± SD (n = 3).
| Moisture (%) | Protein (%) | Ether extract (%) | Crude fiber (%) | Ash (%) | NFE (%) | Gross energy (kJ g-1) |
| 8.51 ± 0.03 | 8.54 ± 0.07 | 0.28 ± 0.03 | 6.06 ± 0.15 | 30.52 ± 0.1 | 85.12 | 10.55 ± 0.02 |
NFE = nitrogen-free extract
Antimicrobial activity. The agar disc diffusion method was used to screen for antimicrobial activity. The EE and F1-F7 fractions were assayed against S. aureus, B. subtilis, E. coli, V. parahaemolyticus, and V. harveyi. None were active against S. aureus, B. subtilis, or E. coli, and only EE and F2 inhibited V. parahaemolyticus and V. harveyi (Table 2). The F2 fraction was fractionated again, and 14 fractions were obtained. Due to the small quantities obtained for some fractions, only some of these could be tested against V. parahaemolyticus and V. harveyi. The results indicate that the F2F6, F2F8, F2F9, and F2F10 fractions were active for both bacteria, while the F2F12 fraction was only active against V. harveyi (Table 3).
Table 2 Antimicrobial activity (zone of inhibition in mm) of the ethanolic extract (EE) and fractions (2 mg/disc) of S. lapazeanum. Mean ± SD (n = 2).
| Extract | Microorganism | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | Bacillus subtilis | Escherichia coli | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | Vibrio harveyi | |
| EE | -- | -- | -- | 8.5 ± 0.70 | 10.0 ± 0 |
| EEF1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| EEF2 | -- | -- | -- | 8.0 ± 0 | 8.5 ± 0.70 |
| EEF3 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| EEF4 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| EEF5 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| EEF6 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 8.75 ± 0.35 |
| EEF7 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 9.0 ± 0 |
| Eritromicina | 25 | 13 | R | 13 | 13 |
| Ampicilina | 10 | R | R | 7 | 7 |
-- Without activity R = Resistant
Table 3 Antimicrobial activity (zone of inhibition in mm) of the EEF2 fractions (2 mg/disc). Mean ± SD (n = 2).
| Fraction | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | Vibrio harveyi |
|---|---|---|
| F2F5 | -- | -- |
| F2F6 | 7.75 ± 0.35 | 10.75 ± 1.06 |
| F2F8 | 8.5 ± 0.71 | 11.75 ± 1.06 |
| F2F9 | 8.0 ± 0.71 | 11.75 ± 0.35 |
| F2F10 | 7.75 ± 0.35 | 11.50 ± 0.71 |
| F2F11 | -- | -- |
| F2F12 | -- | 10.0 ± 0 |
| -- Without activity |
Antioxidant activity. A TLC bioautography was performed to screen for the antioxidant activity of the EE and its fractions. All samples showing discolored bands were considered antioxidants (Fig. 1). For this reason, all samples were analyzed by the colorimetric method to determine the EC50. The results indicate that F6 presented the lowest EC50 of 39.96 μg mL-1, while the highest EC50 corresponded to fraction F1 (394.21 μg mL-1) (Fig. 2). On the other hand, ascorbic acid presented an EC50 of 1.5 μg mL-1, which was 26-fold higher than that of F6.
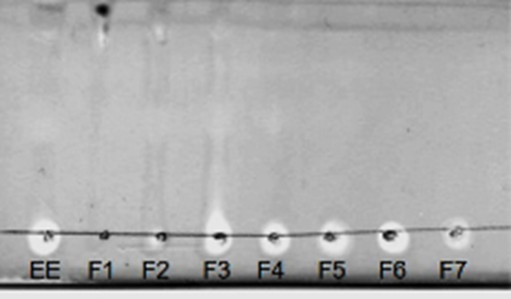
Figure 1 Antioxidant activity of the fractions obtained from the ethanolic extract (EE) of Sargassum lapazeanum using the bioautographic method and revealed with a 0.4% DPPH solution. Discolored areas mean free radical scavenging activity.
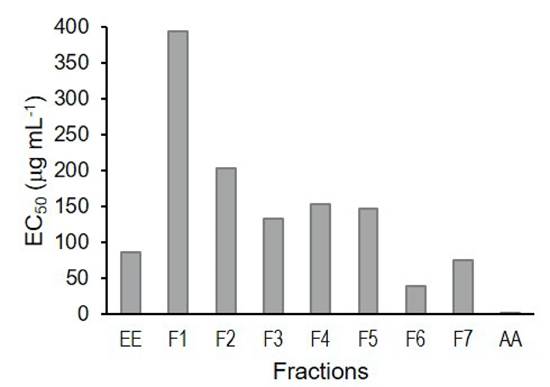
Figure 2 Values obtained for the half maximal effective concentration (EC50) of the fractions of Sargassum lapazeanum obtained by polarity gradient. EE = Ethanolic Extract. AA = Ascorbic acid.
Anticoagulant activity. The CF yield was 3% based on the dry weight of the seaweed. The anticoagulant activity of CF and the CFF1, CFF2, and CFF3 fractions was evaluated, and the results were compared with those of heparin (control) (Table 4). For the APTT assay, all fractions analyzed had clotting times greater than 300 s that were longer than the control (31s). For the TP assay, the CFF2 fraction showed the greatest activity with a coagulation time of 41.9 s; however, all analyzed samples had higher PT values than the control (14 s). Based on the above, the dose-effect curves of the extracts (CF, CFF1, CFF2, and CFF3) were constructed (Fig. 3), and it was observed that most extracts showed coagulation times that were double that of the control (32.8 s) even at minimum concentrations.
Table 4 Fucoidan anticoagulant activity obtained by fractional precipitation. Mean ± SD (n = 3).
| Sample | PT (s) | APTT (s) |
| CF | 30.25 ± 0.79 | > 300 |
| CFF1 | 24.50 ± 1.30 | > 300 |
| CFF2 | 41.93 ± 2.49 | > 300 |
| CFF3 | 23.08 ± 1.90 | > 300 |
| Control | 14.00 | 33.54 |
| PT = prothrombin time, APTT = activated partial thromboplastin time |
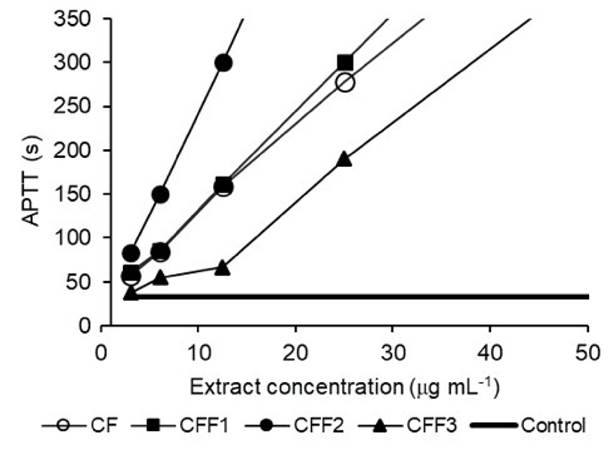
Figure 3 Dose-response curves of anticoagulant activity from the APTT assay employing different fucoidan concentrations from Sargassum lapazeanum and fractions obtained by precipitation.
Fucoidan FTIR. FTIR-ATR spectroscopy was performed to identify the major characteristic peaks (Fig. 4). The CF, CFF1, CFF2, and CFF3 spectra showed different absorption bands that were characteristic of heterofucan. The bands around 1375 and 960-970 cm-1 corresponded to the methyl group of fucose, whereas bands between 1417 and 1616 cm-1 corresponded to an amide bond and uronic acid residues, respectively. An absorption band around 1210-1250 cm-1 corresponding to S‒O stretching, a band at 830 cm-1 corresponding to C‒O‒S stretching, and an additional band at 570 cm-1 confirm a notable number of sulfate groups. Furthermore, the sulfate content in CF, CFF1, CFF2, and CFF3 was 27.85%, 8.10%, 47.48%, and 12.98%, respectively.
Alginate. The sodium alginate yield obtained from the residual algal used for the fucoidan extraction was 22.88% (SD ± 0.91). The viscosity of the alginate obtained was 50.83 mPa·s (SD ± 1.04), and its gel strength was 1807.42 g cm-2 (SD ± 10.60).
DISCUSSION
The main constituents of S. lapazeanum were NFE (85.1%) and ash (30.5%). Usually, NFE is mainly composed of soluble carbohydrates, such as starches and sugars, although it also includes considerable amounts of alginic acid and sulfated polysaccharides (Carrillo-Domínguez et al., 2002). The ash percentage in this study is comparable to those of other studies on seaweeds, which have indicated that the high organic matter content detected is due to these organisms being able to store mineral elements that are abundant in the marine environment (Carrillo-Domínguez et al., 2002; Casas-Valdez et al., 2006).
The protein content reported in the literature for brown macroalgae varies from 3-15% (dry weight) and depends on multiple factors, including the species and season (Burtin, 2003). Studies with Sargassum species have shown that the quality of these proteins is adequate, as essential amino acids are present and digestibility is higher than 70% (Casas-Valdez et al., 2006).
The amount of crude fiber (6.06%) found in this study was low, although comparable to those of some foods intended for human consumption, such as oats (7%) and legumes like beans and chickpeas (5%) (Carrillo-Domínguez et al., 2002). In addition, the amount of gross energy (10.55 kJ g-1) was similar to that found by Di Filippo-Herrera et al. (2018) in S. horridum (10.26-11.55 kJ g-1).
Most studies conducted with crude marine algae extracts mention high activity against gram-positive bacteria, with S. aureus being considered one of the species most susceptible to algal extracts (Ríos et al., 2009). However, the ethanolic extract and fractions obtained by solid-liquid fractionation were not active against the gram-positive bacteria used in the assay. Species of the Sargassum genus, such as S. oligocystum Montagne (Baleta et al., 2011) and S. latifolium (Turner) C. Agardh (Dashtiannasab et al., 2012), have shown high potential against bacteria of the Vibrio genus. However, these differences in activity can be explained by several factors, such as the species studied, seasonal variation, geographic variation, reproductive state of the algae (De Lara-Issasi & Álvarez-Hernández, 1999), and the type of solvent used for the extraction (Tüney et al., 2006). In addition, some studies have shown that V. harveyi is usually sensitive to antibacterial activity tests, presenting more defined inhibition halos than those observed for V. parahaemolyticus (Baleta et al., 2011; Dashtiannasab et al., 2012).
Antibacterial activity of S. lapazeanum was present in both polar and non-polar fractions. However, the F2 (non-polar) fraction was selected for fractionation, as it showed the highest activity against V. parahaemolyticus and V. harveyi. After fractionation, the antibacterial activity in some subfractions increased, reflected in more defined inhibition halos. Fractions F2F8 and F2F9 were the most active against V. harveyi (11.75 mm), while fraction F2F8 was most active against V. parahaemolyticus (8.5 mm). This shows that the fractionation process was effective in such a way that activity increased. The selective activity against bacteria of the Vibrio genus observed in this study suggests that S. lapazeanum may be considered as an alternative species to obtain natural antibacterial compounds with applications in the treatment of vibriosis in aquaculture settings (Rubio-Limonta & Silveira-Coffigny, 2012). In a qualitative comparison, it was observed that the fractions of the extracts presented a higher antimicrobial activity than the ampicillin control and lower than the erythromycin control.
The results of the free radical scavenging activity assays showed that S. lapazeanum is a potential source of compounds with antioxidant activity, although the activity of the fraction (CFF2) with the highest activity (EC50 = 39.96 µg mL-1) was 6-fold lower than that found by Zubia et al. (2007) who obtained EC50 values of 6.64 and 7.14 μg mL−1 for S. ramifolium Kützing and S. pteropleuron Grunow, respectively.
Generally, photoautrophic organisms are exposed to high oxygen and radical stresses and have adapted to these conditions by developing various yet efficient protective systems against reactive oxygen species and free radicals. Some of these systems consist of the production of powerful antioxidants, such as polyphenols, carbohydrates, nitrogenous compounds, phytosterols, carotenoids, chlorophyll derivatives, and other photoprotective pigments (Zubia et al., 2007).
The IR spectra of the fucoidan fractions presented similar absorption patterns, suggesting that all fractions contain the same functional groups; however, differences in composition were present, as evidence by the differences among the intensities of the absorption peaks. The band at 830 cm−1 was assigned to the vibration of the C-O-S group, indicating the presence of a sulfate group in the axial position of C4 with minor substitutions in carbons C2 and C3 of fucose given the less intense absorption peak at 805 cm-1 (Li et al., 2008). Furthermore, the absorption band at 570 cm-1 confirmed the presence of a notable number of sulfate groups (Synytsya et al., 2010). As such, the fucoidan obtained from S. lapazeanum is described as a heterofucan due to the presence of uronic acids (1600-1650 cm-1) and neutral sugars (1180-1000 cm-1) in the IR bands.
The results obtained from the PT and APTT assays demonstrated the high anticoagulant potential of S. lapazeanum, as all of the extracts prolonged the clot formation time, extending it to double that of the control, even at minimum concentrations. The fucoidan fractions obtained in the present study showed activities similar to that of heparin, according to the study by Ronghua et al. (2003) who reported a coagulation time for heparin of 125 s at concentrations of 10 μg mL-1. Based on this, it can be said that CFF2 was the most active fraction with the greatest potential, as it doubled this time at the same concentration. This agrees with the potential observed in S. vulgare C. Agardh, which was reported to be 10-fold more active than heparin (Guerra-Dore et al., 2013). Heparin is a biomolecule that contains highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan and is the most widely used anticoagulant on the market for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. However, the prolonged use of heparin compounds can have adverse effects, such as thrombocytopenia, osteoporosis, and bleeding (Gómez-Ordóñez, 2012).
Regarding the degree of sulfation, the sulfate content in CFF2 (47.48%) was higher compared to those of the other fractions in this study and also presented the most activity. This agrees with the results of previous studies that have indicated that an increase in sulfate content is one of the most important factors that determines anticoagulant activity, which increases according to the degree of fucan sulfation (Muñoz-Ochoa et al., 2009). However, further studies are needed to determine its potential application in humans.
Lastly, the alginate yield (22.8%) obtained from S. lapazeanum is high when compared with that reported for S. cymosum C. Agardh (15.9%), S. sinicola (13-15%), and S. vulgare (16.9%; Camacho & Hernández-Carmona, 2012; Torres et al., 2007; Yabur et al., 2007). Due to their thickening, gelling, stabilizing, and film-forming properties, alginates are widely used in food, textile, and pharmaceutical industries (Hernández-Carmona et al., 2012). The results of the present study showed that Sargassum lapazeanum is an alga with a high potential as a source of compounds with antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticoagulant activity.











 nueva página del texto (beta)
nueva página del texto (beta)




