1. Introduction
The Cerro Quema deposit located in the Azuero Peninsula (SW Panama) consists of several mineralized bodies. From west to east, these include La Pava, Cerro Quemita, Mesita, and Cerro Quema (Figure 1). Global measured, indicated, and inferred resources for the Cerro Quema deposit (four orebodies) include a total oxide resource of 24.60 Mt @ 0.71 g/t Au and 0.04% Cu, and a total sulfide resource of 11.38 Mt @ 0.41 g/t Au and 0.31% Cu (Sutcliffe et al., 2014). Ore grade and tonnage are variable through the different orebodies. This variability can be summarized as follows (Sutcliffe et al., 2014):
La Pava measured, indicated, and inferred oxide resources: 18.28 Mt @ 0.66 g/t Au and 0.04% Cu. Measured, indicated, and inferred sulfide resources: 8.54 Mt @ 0.39 g/t Au and 0.36% Cu.
Cerro Quemita + Cerro Quema + Mesita indicated and inferred oxide resources: 6.32 Mt @ 0.83 g/t Au and 0.03% Cu. Indicated and inferred sulfide resources: 2.84 Mt @ 0.47 g/t Au and 0.15% Cu.
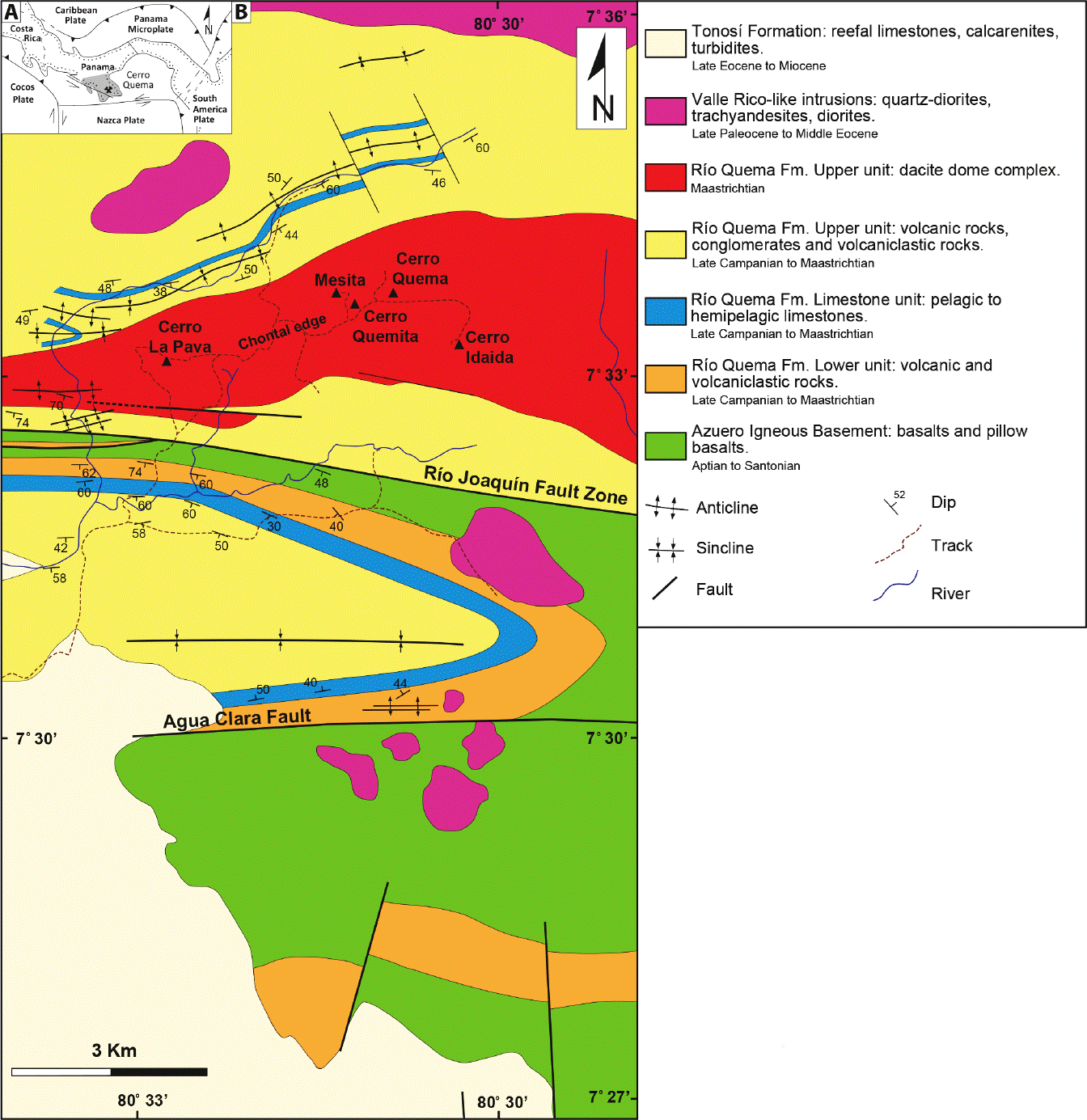
Figure 1 (A) Plate tectonic setting of south Central America (Azuero Peninsula is shaded). (B) Simplified geologic map of central Azuero Peninsula and location of the Cerro Quema Au-Cu deposit (after Corral et al., 2013, 2016).
Additional orebodies have been discovered to the east of Cerro Quema; however, their resources have not yet been assessed.
Although several studies have been performed on the geology of the deposit (Leach, 1992; Horlacher and Lehmann, 1993; Torrey and Keenan, 1994; Nelson, 1995; Corral et al., 2011), on its origin and evolution (Corral et al., 2016, 2017), and on the metallogenic potential of the Azuero Peninsula (Del Giudice and Recchi, 1969; Ferenčić, 1970; Kesler et al., 1977; Corral et al., 2016), there is still a gap in the knowledge of the trace metal composition of the Cerro Quema Au-Cu ore.
Lithocaps associated with high-sulfidation epithermal deposits can have large extensions of advanced argillic altered rocks (> 20 km2). However, typically only a small portion of the lithocap is mineralized, and due to the lack of directional indicators, exploration in this environment can be difficult (Sillitoe, 1995; Corbett and Leach 1998; Chang et al., 2011). The study of the concentrations and distribution of metals in ore deposits is an essential tool for greenfield and brownfield exploration. Many deposits may contain anomalous concentrations of metals other than those of primary economic interest (Kesler et al., 2003), and these metals can be used as prospective guides to high-grade mineralization. High-sulfidation epithermal deposits commonly contain economically important amounts of Au, Ag, and Cu, as well as significant tenors of As, Sb, Hg, Sn, Te, and Bi (e.g., Arribas, 1995; Arribas et al., 1995; Kesler et al., 2005). Although these elements are probably of magmatic origin (e.g., Heinrich et al., 2004), they may vary significantly in relative abundance within individual deposits. This suggests that the fluid composition changed throughout the lifespan of the magmatic-hydrothermal system (Deditius et al., 2009) possibly due to water-rock interaction, or cooling/mixing processes.
Geochemical data of trace elements in high-sulfidation epithermal ores has been reported for decades (e.g., Rodalquilar: Hernandez et al., 1989; Nansatsu: Hedenquist et al., 1994; Pueblo Viejo: Kesler et al., 2003, Sillitoe et al., 2006; Cerro de Pasco: Baumgartner et al., 2008; Martabe: Sutopo, 2013). Here we present a case study of the metal content of the Cerro Quema Au-Cu deposit. We use whole-rock geochemical analysis of ore samples to better understand the deposit enrichment, its metal distribution and association of metals and minerals. Furthermore, we present useful criteria for exploration of high-sulfidation Au-Cu deposits.
2. Geologic setting
2.1. Regional geology
The Cerro Quema high-sulfidation epithermal Au-Cu deposit covers an area of ~20 km2 in the center of the Azuero Peninsula (Figure 1). The mineralization is hosted in the dacite dome complex of the Río Quema Formation (late Campanian to Maastrichtian; Corral et al., 2013, 2016).
As described in Buchs et al. (2010, 2011) and Corral et al. (2011, 2013), the Azuero Arc Group (late Cretaceous to Eocene) overlies the Azuero Igneous Basement (Conacian to Santonian) and is discordantly overlapped by the Tonosí Formation (Eocene to Miocene). The Río Quema Formation is a volcanosedimentary sequence that represents the earliest calc-alkaline volcanism of the Azuero Arc Group. In the Cerro Quema area, this sequence is bounded to the north by the Valle Rico batholith, a series of Eocene (55-49 Ma; Del Giudice and Recchi, 1969; Kesler et al., 1977; Lissinna, 2005; Montes et al., 2012; Corral et al., 2016) diorite and quartz diorite intrusions with calc-alkaline affinity. The Late Cretaceous Azuero Igneous Basement (Aptian to Santonian; Kolarsky et al., 1995; Kerr et al., 1997; Hoernle et al., 2002; Lissinna, 2005; Buchs et al., 2010) comprises tholeiitic basalts and pillow basalts with oceanic plateau affinity that bounds the Río Quema Formation to the south (Figure 1). A complete geochemical characterization of the igneous rocks of the Azuero Peninsula is provided by Hoernle et al. (2002, 2004), Lissinna, (2005), Wörner et al. (2009), Buchs et al. (2010, 2011), Corral et al. (2010, 2011), and Wegner et al. (2011). The main tectonic structures in the district include the east-trending Agua Clara and Río Joaquín Fault zones. An extensive network of minor northwestto northeast-trending subvertical faults with normal dip-slip and minor strike-slip components are observed. In addition, mesoscale southwest-plunging open folds with moderately dipping limbs are observed. Overall, the structures suggest dextral transpression with dominant reverse dipslip motion during late Campanian to middle Eocene time (Corral et al., 2013).
2.2.1. Exploration history
In 1965, a regional study of the geology and metallogeny of Panama financed by the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) was undertaken to evaluate Panama’s mineral resources potential. Results in the Azuero Peninsula (e.g., Del Giudice and Recchi, 1969) revealed areas with significant copper and gold anomalies that were related to porphyry copper and epithermal deposits. These findings were later confirmed by Ferenčić (1970, 1971) and Kesler et al. (1977). In 1986-1988, the Compañía de Exploración Mineral S.A. (CEMSA) further investigated the area and eventually discovered Cerro Quema, which was considered a potentially mineable target. From 1990 to 1994, Cyprus Amax Minerals carried out several exploration programs including both soil geochemistry and drilling campaigns (4622 m of core drilling and 17579 m of RC drilling). In 1996, Campbell Resources Inc. carried out an infill drilling program to further define the resources (1750 m of core drilling), and completed a Project Feasibility Study. By 2007, Bellhaven Copper & Gold Inc. acquired the project, and completed a feasibility study for the project together with metallurgical tests. Pershimco Resources Inc. acquired the project in 2010 and drilled 16939 m of core drilling in 79 holes and 32728 m of RC drilling in 330 holes. Additionally, the company completed a lithological and structural mapping of the area, and performed channel sampling and geochemical sampling. Several geophysical surveys have been carried out including an Induced Polarization (IP) survey as well as airborne radiometric, magnetic, and VTEM surveys (e.g., Kwan et al., 2016). In 2016 Pershimco Resources Inc. merged with Orla Mining Ltd. to continue the exploration and development of the Cerro Quema project under the name Orla Mining Ltd.
2.2.2. Hydrothermal alteration
Hydrothermal alteration at Cerro Quema follows an eastward trend that is parallel to secondary faults related to the Río Joaquín Fault Zone. It is defined by several concentric alteration halos that are mainly restricted to dacite domes of the Río Quema Formation, which have higher porosity and permeability than other rock types of the volcano-sedimentary sequence (Corral et al., 2017). According to Corral et al. (2011, 2016), four distinct alteration zones can be identified at Cerro Quema: several vuggy quartz centers (up to ~600 m in length) and local advanced argillic alteration zones (up to ~250 m in length) are observed within the central core of the deposit, enclosed by an argillic alteration zone (up to ~1900 m in length). The propylitic alteration forms an outermost halo surrounding the argillic alteration zone. Vuggy quartz alteration consists of a groundmass of microcrystalline anhedral quartz grains with disseminated pyrite, chalcopyrite, enargite, tennantite, barite, minor rutile, and trace sphalerite. In this alteration, the morphology of the vugs varies from idiomophic (hornblende and feldspar shape) to irregular, and their abundance generally reflects the presence of hornblende and feldspar phenocrysts in the volcanic host rock. The advanced argillic alteration zone is characterized by quartz, alunite supergroup minerals (e.g., alunite, natroalunite, aluminum phosphate-sulfate minerals), dickite, pyrophyllite, barite, illite, and minor diaspore and rutile. Argillic alteration produced quartz, kaolinite, illite, illite-smectite, and minor chlorite with local disseminated pyrite. The propylitic alteration zone contains chlorite, epidote, calcite, rutile, pyrite, chalcopyrite, and minor hematite and magnetite. Stable isotope (S, O, H) geochemistry and fluid inclusion studies revealed that hydrothermal alteration at Cerro Quema was produced by magmatic-hydrothermal fluids that were variably mixed with meteoric fluids (Corral et al., 2017).
2.2.3. Mineralization
Mineralization at Cerro Quema can be subdivided into two different zones: (A) hypogene mineralization, produced by magmatic-hydrothermal fluids; and (B) supergene mineralization, produced by oxidation of the hypogene mineralization as well as by the precipitation of secondary sulfides. The different mineralization types and their distribution are fully described in Corral et al. (2016, 2017), and can be summarized as follows.
Hypogene mineralization
Hypogene mineralization is generally developed below the oxidized zone, but due to the rough and steep topography, small (meter scale) outcrops are locally found at the surface. Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide, although there is a diverse group of accompanying sulfides (e.g., enargite, tennantite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and bornite) also associated with the Au-Cu mineralization.
Based on field and petrographic observations, hypogene mineralization has been divided into five stages, where stages 3 and 4 contain the majority of the metals. Stage 1 consists of disseminated, fine-grained, idiomorphic and subidiomorphic pyrite, accompanied by rutile and barite in vugs and disseminations, with minor enargite, tennantite, and chalcopyrite at depth (Figures 2B, 4A, 4C). Sphalerite occurs as a trace mineral disseminated in the groundmass. Stage 2 is composed of disseminated pyrite in the cement of a hydraulic breccia, associated with alunite-natroalunite, dickite, and traces of chalcopyrite. Stage 3 consists of veinlets of pyrite, chalcopyrite, enargite, and tennantite that crosscut stages 1 and 2. Textures observed in Stage 3 veinlets show that pyrite is replaced by enargite, enargite is replaced by tennantite, and finally tennantite is replaced by chalcopyrite. Bornite occurs as a trace mineral. Stage 4 occurs as ~5 cm thick breccia bands, composed of pyrite, chalcopyrite, and minor enargite. The Stage 4 breccia bands crosscut all the previous stages. Stage 5 consists of 5 to 10 cm thick base metal sulfide-rich veins composed of pyrite, quartz, and barite together with minor chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena. Gold occurs as submicroscopic grains and as invisible gold within pyrite. Copper is associated with Cu-bearing sulfides and sulfosalts such as chalcopyrite, enargite, bornite, and tennantite.
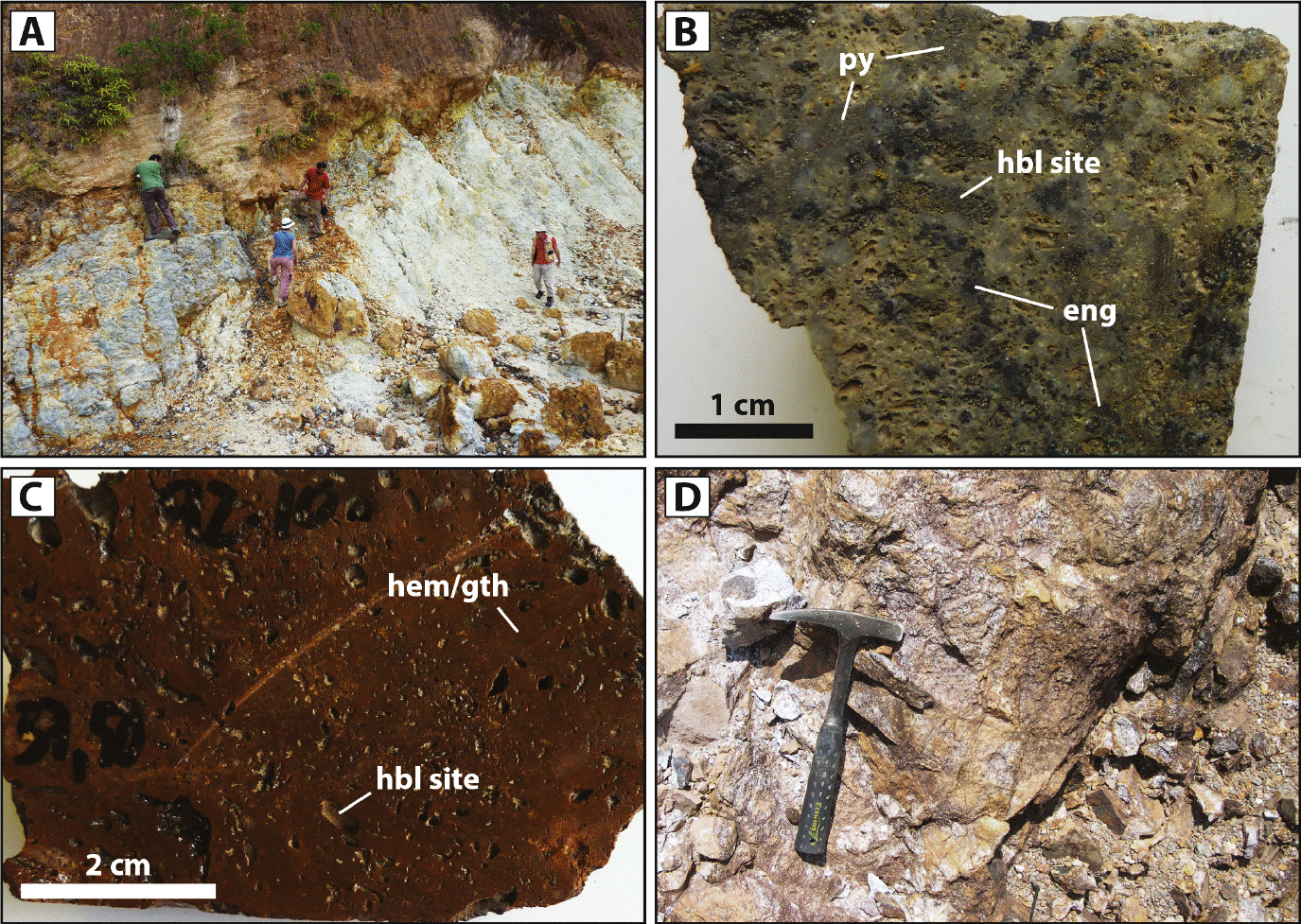
Figure 2 Examples of ore zones at Cerro Quema. (A) Oxidation boundary developed on the advanced argillic alteration zone. (B) Sulfide ore in drill hole (sample 9343-77; 0.31 g/t Au, > 1.0% Cu). (C) Oxide ore in drill hole (sample 9210-37.50; 2.07 g/t Au, 0.11% Cu). (D) Oxide ore in outcrop (sample LP-235; 0.51 g/t Au, 0.11% Cu). Mineral abbreviations according to Whitney and Evans (2010): hbl site = hornblende site, hem/gth = hematite/goethite, eng = enargite, py = pyrite.
Supergene mineralization
Intense weathering has affected fresh and hydrothermally altered rocks in the Cerro Quema area down to depths of 150 m (Figure 2A). Weathering of the high-sulfidation ore has developed a thick quartzand iron oxide-rich zone that overprints the primary sulfide-bearing zone. Quartz is relict of the hypogene hydrothermal alteration zone, and was not directly produced by the weathering or oxidation processes. This oxidized zone is developed in the upper part of the orebodies. It is characterized by vuggy quartz containing abundant hematite and goethite within the groundmass. The hematite and goethite replace the cement of hydrothermal breccias, and fill the vugs. Hypogene pyrite, barite, and rutile remain as trace minerals in the oxidation zone. Gold has been found as submicroscopic grains (< 1 μm), which prevented quantitative analysis of its chemical composition. Below the oxidation zone, supergene enrichment has caused deposition of secondary Cu-bearing minerals such as chalcocite and minor covellite. The secondary Cu sulfides are found replacing chalcopyrite, tennantite, and enargite as well as filling small fractures.
2.2.4. Age of the Cerro Quema deposit
The age of Cerro Quema has been constrained from crosscutting relationships between the volcanic host rocks combined with biostratigraphic and Ar-Ar geochronological data. Ore formation is estimated to be Eocene (~55-49 Ma) in age and it is interpreted to be related to subvolcanic porphyry intrusions contemporaneous with the Valle Rico batholith (Corral et al., 2016).
3. Results of the Cerro Quema metal content
3.1. Sampling and analytical methods
To study the geochemical compositions of the different Au-Cu ores at Cerro Quema, the samples have been subdivided into two groups according to their origin and metallurgical properties:
A total of 34 representative samples of the sulfide ore (n = 11) and of the oxide ore (n = 23) were collected in different mineralized zones of Cerro Quema. Most samples belong to the vuggy quartz alteration zones; however, some samples from the advanced argillic (n = 2) and argillic (n = 1; Table 1) alteration zones are also included. Whole rock geochemical analyses of Au, Ag, Cd, Cu, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Zn, S, As, Ba, Hg, Sb, and W concentrations were performed by INAA and with an aqua regia digestion followed by ICP-MS analysis on 30 g sample spits at Activation Laboratories, Canada [Code 1 EPI (Au+14)]. Certain elements such as Mn and Hg mostly show concentrations below the analytical detection limit and therefore we have not considered them in the statistical calculations. Sample 9349-77 has a Cu content above the upper limit of detection (10000 ppm), therefore this value has been used as the minimum Cu content of the sample. Additionally, as samples were reduced to powder using a tungsten carbide mill, W concentrations should be regarded only as semi-quantitative due to possible contamination caused by the sample preparation method. The complete dataset of the analyzed rock, including the ore group and hydrothermal alteration zone, is presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Summary of the analyzed samples, location, hydrothermal alteration, and trace element content. Abbreviations: AA = Argillic Alteration, AAA = Advanced Argillic Alteration, VQ = Vuggy Quartz Alteration, bdl = below detection limit.
3.2. Whole-rock data
The results show that the oxide ore has the highest concentrations of Au (2.4 g/t), Ag (2.0 g/t), Pb (432 ppm), and Sb (317 ppm), whereas the sulfide ore has the highest concentrations of Cu (> 1%), Zn (403 ppm), As (2.74%), Cd (15.2 ppm), and S (10.12%).
The average concentrations of elements in the oxide and sulfide ores divided by their average concentrations in the genetically related country rocks (i.e., diorites and quartz diorites; Corral et al., 2011) has been used as an indicator of the deposit enrichment factor (Table 2). Certain elements such as Ag, Cd, Pb, As, and Hg show concentrations below the detection limits in the country rocks, and therefore they have not been considered for the enrichment factor calculations. The enrichment factor of the oxide/sulfide ore was calculated by dividing the average concentration of elements in the oxide ore with their average concentration in the sulfide ore (Table 2).
Table 2 Average enrichment factors for the oxide and sulfide ores with respect to the country rocks from Corral et al., (2011), and average enrichment factors of the oxide zone with respect to the sulfide zone. Element concentrations are expressed in ppm except for Au which is expressed in ppb.
| Au | Cu | Ag | Pb | Ni | Zn | S | As | Ba | Sb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country rock average (n = 6) | 7.93 | 125.43 | - | - | 16.00 | 68.43 | 0.01 | - | 351.71 | 0.19 |
| Sulfide Ore enrichment (n = 11) | 36.55 | 9.59 | - | - | 0.46 | 0.75 | 582.06 | - | 97.06 | 104.12 |
| Oxide Ore enrichment (n = 23) | 88.00 | 5.88 | - | - | 0.17 | 0.08 | 26.10 | - | 9.24 | 219.58 |
| Oxide/Sulfide Ore enrichment | 2.41 | 0.61 | 1.24 | 1.86 | 0.37 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 2.11 |
The enrichment factors of mineralized rocks with respect to the country rock are up to 88 for Au and up to 9.59 for Cu. Although Au and Cu are the elements of economic interest in the Cerro Quema deposit, the highest enrichment factor with respect to the country rock is shown by Sb (219), Ba (97), and S (582). Other elements such as Zn (0.08) and Ni (0.17) are depleted with respect to the country rocks. The enrichment factors of the oxide ore with respect to the sulfide ore show that Au (2.41), Sb (2.11), Pb (1.86), and Ag (1.24) are primarily concentrated in the oxide zone, whereas Cu (0.61), Ni (0.37), As (0.30), Zn (0.11), Ba (0.10), and S (0.04) are primarily concentrated in the sulfide zone.
Correlation coefficients (Table 3) between element pairs were used to define element affinities and their mineral correlation. Due to the skewed population shown by the element concentrations, calculations for element correlation were performed after previous transformation to log values as suggested by Kesler et al. (2003). In this study, correlation coefficient ranges have been defined as strongly correlated (r > 0.90), well correlated (0.60 < r < 0.89), and poorly correlated (0.40 < r < 0.59).
Table 3 Correlation coefficients (r) of trace and major elements at Cerro Quema. Correlations were calculated for elements transformed to log values. Superindex indicates: a = strongly correlated, b = well correlated, c = poorly correlated.
| Au | Ag | Cd | Cu | Mo | Ni | Pb | Zn | S | As | Ba | Sb | |
| Oxide Ore | ||||||||||||
| Au | 1.00 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.36 | -0.04 | 0.37 | -0.02 | 0.10 | 0.1 | 0.00 | 0.07 | -0.08 |
| Ag | 1.00 | -0.34 | -0.31 | 0.43c | -0.25 | -0.32 | 0.09 | -0.42 | -0.11 | 0.06 | -0.22 | |
| Cd | 1.00 | 0.57c | 0.27 | 0.58c | -0.30 | 0.01 | 0.33 | -0.05 | 0.22 | -0.10 | ||
| Cu | 1.00 | 0.16 | 0.83b | -0.01 | 0.53c | 0.71b | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.10 | |||
| Mo | 1.00 | 0.24 | -0.35 | 0.25 | 0.06 | -0.24 | 0.28 | -0.42c | ||||
| Ni | 1.00 | -0.02 | -0.14 | 0.48c | 0.18 | 0.34 | 0.13 | |||||
| Pb | 1.00 | 0.31 | -0.21 | 0.37 | -0.13 | 0.35 | ||||||
| Zn | 1.00 | 0.62b | 0.38 | 0.20 | 0.05 | |||||||
| S | 1.00 | 0.05 | 0.46c | -0.16 | ||||||||
| As | 1.00 | -0.07 | 0.60b | |||||||||
| Ba | 1.00 | -0.32 | ||||||||||
| Sb | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| Au | Ag | Cd | Cu | Mo | Ni | Pb | Zn | S | As | Ba | Sb | |
| Sulfide Ore | ||||||||||||
| Au | 1.00 | 0.82b | 0.05 | 0.06 | -0.33 | -0.07 | 0.62b | -0.05 | -0.12 | 0.32 | 0.65b | 0.40c |
| Ag | 1.00 | 0.29 | 0.23 | -0.48c | -0.02 | 0.68b | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.40c | 0.58c | 0.31 | |
| Cd | 1.00 | 0.79b | -0.23 | 0.74b | 0.43c | 0.89b | 0.72b | 0.74b | -0.43c | 0.16 | ||
| Cu | 1.00 | 0.05 | 0.77b | 0.40c | 0.90a | 0.90a | 0.71b | -0.12 | 0.00 | |||
| Mo | 1.00 | -0.17 | -0.67b | -0.09 | -0.10 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.32 | ||||
| Ni | 1.00 | 0.30 | 0.41c | 0.89a | 0.46c | -0.36 | -0.08 | |||||
| Pb | 1.00 | 0.90a | 0.40c | 0.38 | 0.43c | 0.08 | ||||||
| Zn | 1.00 | 0.92a | 0.71b | -0.35 | 0.01 | |||||||
| S | 1.00 | 0.51c | -0.21 | 0.15 | ||||||||
| As | 1.00 | -0.11 | 0.52c | |||||||||
| Ba | 1.00 | -0.14 | ||||||||||
| Sb | 1.00 | |||||||||||
As shown in Table 3, the most significant correlations in the oxide ore are as follows: As is well correlated with Sb; S is well correlated with Cu and Zn and poorly correlated with Ba. On the other hand, the most significant correlations in the sulfide ore are as follows: Au is well correlated with Ag, Pb, and Ba, and poorly correlated with Sb; Ag is well correlated with Pb and poorly correlated with As and Ba; Cu is strongly correlated with Zn, well correlated with Cd and As, and poorly correlated with Pb; finally, S is strongly correlated with Cu, Ni, and Zn.
4. Discussion on the trace element distribution
According to Corral et al. (2016, 2017), field, petrologic, and isotopic observations point towards a magmatic-hydrothermal fluid as the precursor of the mineralization and hydrothermal alteration. Later processes such as weathering and oxidation affected the hypogene minerals, leading to the development of the oxide ore.
In the sulfide ore, Au is well correlated with Ag, Pb, and Ba (Table 3; Figure 3A, 3B). Assuming that Au is present as invisible gold associated with the pyrite lattice (Corral et al., 2011, 2016), the Au-Ba positive correlation (0.65) suggests that Au-bearing pyrite is associated with the presence of barite (Figure 4A, 4B). The high Ba enrichment in the sulfide zone with respect to the country rocks (97 times; Table 2) indicates that Ba was introduced by the hydrothermal fluid. Minor amounts of Ba could have also been liberated from feldspars during advanced argillic alteration processes. This contrasts with the Pueblo Viejo deposit (Kesler et al., 2003) where Au and Ba are not well correlated (0.12).
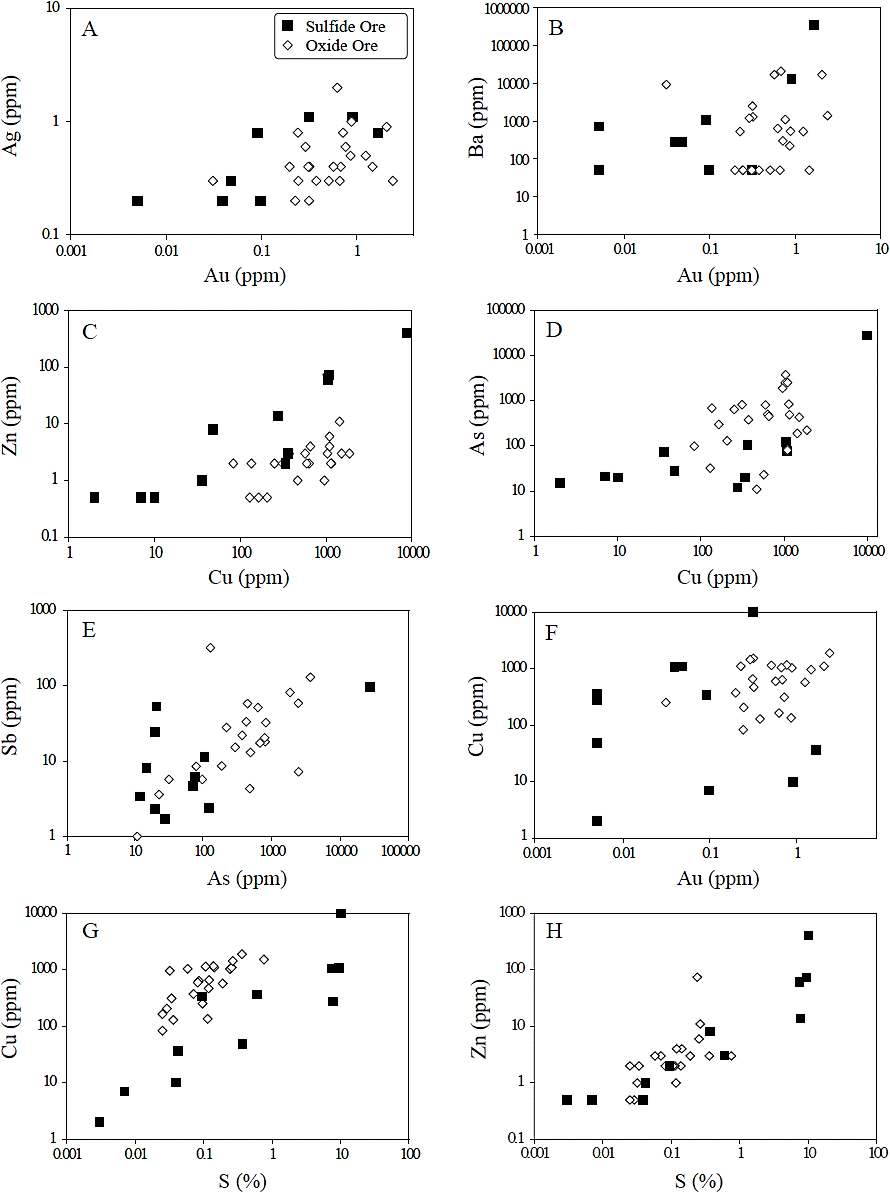
Figure 3 Correlation plots between element pairs. (A) Au-Ag. (B) Au-Ba. (C) Cu-Zn. (D) Cu-As. (E) As-Sb. (F) Au-Cu. (G) S-Cu. (H) S-Zn. Symbols for all graphs: squares = sulfide ore; diamonds = oxide ore.
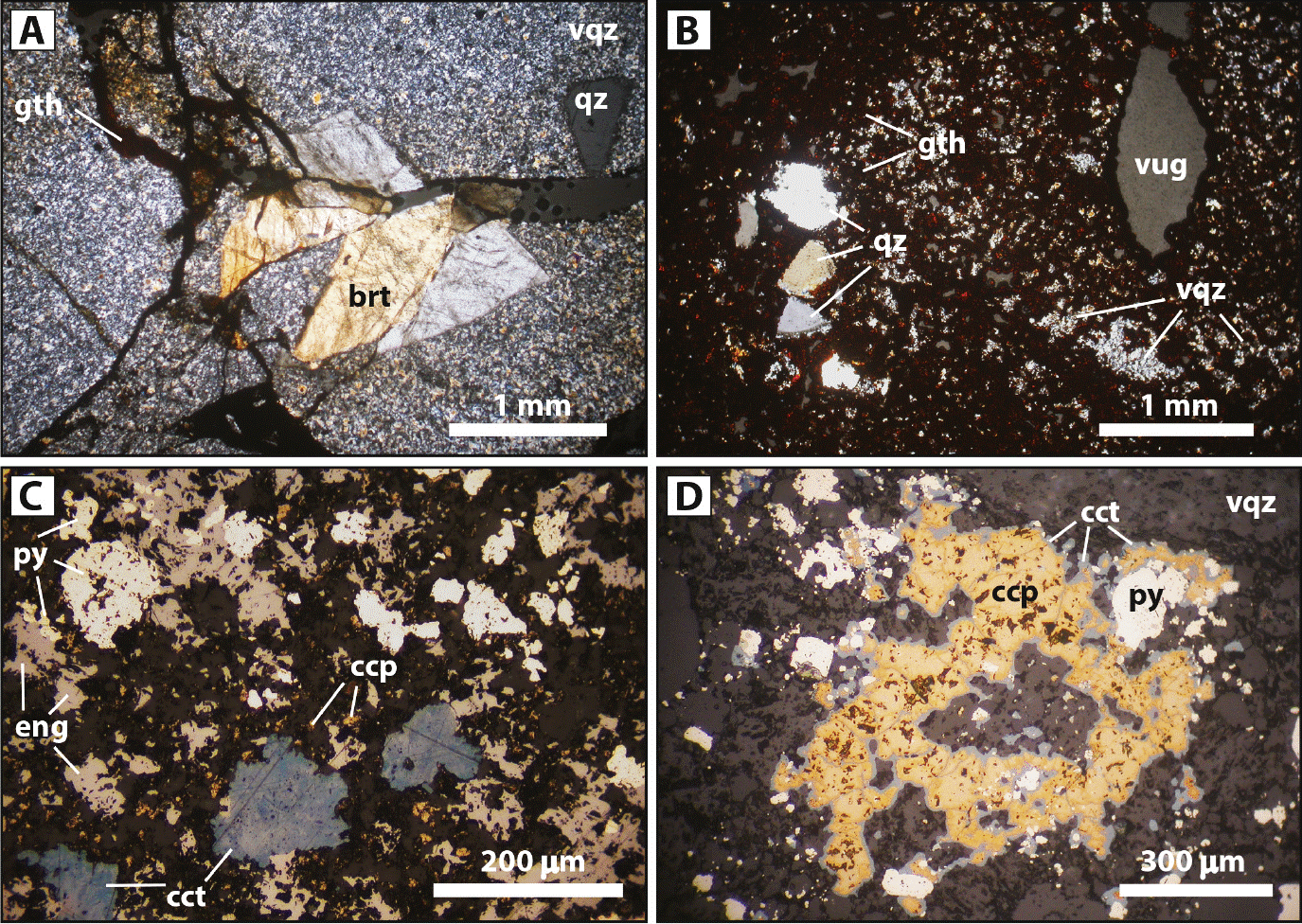
Figure 4 Microphotographs of Cerro Quema ores. (A) Oxide ore: oxidized vuggy quartz altered dacite with barite and elevated gold grade (sample 9322-34; 0.68 g/t Au, 21000 ppm Ba; cross-polarized transmitted light). (B) Oxide ore: massively oxidized vuggy quartz altered dacite (sample 9210-121; 2.40 g/t Au, 1400 ppm Ba; cross-polarized transmitted light). (C) Sulfide ore: detail of a sulfide microveinlet (Stage 3) constituted by pyrite, enargite, and minor chalcopyrite. Chalcocite replaces enargite. Host rock is a vuggy quartz altered dacite (sample 0308-111.60; 1.68 g/t Au; reflected polarized light). (D) Sulfide ore: detail of a breccia band (Stage 4) constituted by pyrite and chalcopyrite. Chalcocite replaces chalcopyrite. Groundmass is a vuggy quartz altered dacite (reflected polarized light). Mineral abbreviations according to Whitney and Evans (2010): brt = barite, ccp = chalcopyrite, cct = chalcocite, eng = enargite, gth = goethite, py = pyrite, qz = quartz phenocryst, vqz = vuggy quartz alteration.
Au and Ag are also well and positively correlated (Figure 3A) suggesting the presence of both elements within the pyrite lattice. As the Ag content in the whole rock is up to 1.1 ppm (sample 9311-153), and up to 400 ppm in pyrite (Corral et al., 2016), the Ag content in the mineralized rock seems to be related to the presence of disseminated pyrite. Correlation of Au with Pb is not fully understood; however, Pb could be related to the presence of hokutolite (Pb-bearing barite), which usually occurs in hot spring environments (Hokuto and Peito hot spring, Taiwan and Tamagawa hot spring, Japan; Okamoto, 1911; Sasaki and Minato, 1982; Momoshima et al., 1997) and in high-sulfidation deposits (Mt. Carlton, Australia; Sahlström et al., 2017). As previously mentioned, is related to high gold grades. Cu is strongly correlated with Zn, well correlated with Cd and As, and poorly correlated with Pb (Table 3; Figure 3C, 3D), suggesting that Cu may be associated with cupriferous pyrite (up to 3.67 wt% Cu and up to 311 ppm Cd; Corral et al., 2016) and also likely with chalcopyrite containing sphalerite inclusions. The good and positive correlation between Cu and As is explained by the presence of enargite (Figures 3D, 4C) and other Cu-bearing sulfosalts (e.g., tennantite), which could also explain the correlation of Cu and As with Zn and Ag and of Sb with As (Figure 3E). The lack of strong correlation between Cu and Au (Figure 3F) may be due to the presence of these elements in different minerals such as Au occurring within the pyrite lattice, whereas Cu is associated with Cu-bearing minerals (e.g., chalcopyrite, enargite and tennantite; Figure 4C, 4D). The strong correlations of Zn with Cu, Pb, and S, and Cu with S (Figure 3G, 3H), are caused by the presence of disseminated sphalerite and/or as sphalerite inclusions in pyrite/chalcopyrite, which could also explain the good correlation of Zn with Cd and As.
The element distribution and correlations observed in the oxide ore strongly differ from those in the sulfide ore. Weathering and oxidation of the sulfide ore produced dissolution of cupriferous pyrite, chalcopyrite, enargite, and tennantite, resulting in the concentration of Au, Ag, Pb, and Sb (likely immobile elements), and in the bleaching of Cd, Cu, Zn, and As (likely more mobile elements). In the oxide zone, Au and Ag are not well correlated with each other nor with other trace elements (Table 3), which could be explained from the difference in element mobility during mineral dissolution/precipitation/remobilization (e.g., Andreu et al., 2015). Contrary to the sulfide ore, Au and Ba are not well correlated in the oxide ore (0.65 and 0.07, respectively). However, they still show an overall positive slope in the correlation plots, indicating that the highest Au concentrations match with the highest Ba concentrations (Figure 3B). Barite has been described as associated with gold in other high-sulfidation epithermal deposits such as El Indio-Tambo (Chile; Siddeley and Araneda, 1990; Jannas et al., 1990, 1999), Summitville (Colorado; Steven and Ratté, 1960; Stoffregen, 1987), Chinkuashih (Taiwan; Huang, 1955, 1962), and Furtei (Sardina; Ruggieri, 1992, 1993; Ruggieri et al., 1997). Anomalous concentrations of Ba could, therefore, be a prospective guide to high-grade Au mineralization in high-sulfidation epithermal deposits.
As and Sb are strongly correlated (Figure 3E) and do not correlate well with other trace elements, suggesting that As and Sb could be present as oxides/hydroxides in this ore. Cu is well correlated with Ni and S suggesting they are associated with relicts of disseminated pyrite of the sulfide ore (up to 3.67 wt% Cu and 4300 ppm Ni; Corral et al., 2016). S and Zn are well correlated, which is explained by the observed although scarce disseminated sphalerite.
Only two analyzed samples have Hg contents above the detection limit (11 and 6 ppm). As Hg is commonly partitioned into a rising vapor phase by boiling (Barnes and Seward, 1997), the observed low concentrations of Hg may suggest that the present day exposure at Cerro Quema represents a relatively deeper portion of the hydrothermal system, and that the shallowest portion of the system has been eroded.
5. Summary and implications for exploration
Weathering and oxidation processes at the Cerro Quema deposit led to the development of two distinct ore zones. An upper iron oxide-rich zone (oxide ore), where Au, Ag, Pb, and Sb are concentrated, is characterized by goethite-hematite, free gold (Au ± Ag), relicts of disseminated pyrite and sphalerite, and barite (associated with elevated Au grades). A lower sulfide-rich zone (sulfide ore), where Cu, Cd, Zn, Ni, and As are concentrated, is constituted by auriferous pyrite (± Cu-Ag), chalcopyrite (± sphalerite inclusions), enargite-tennantite, secondary copper sulfides (e.g., chalcocite, covellite), and barite.
In terms of exploration, the most significant observation from the trace element distribution and correlation factors is that exploration for Au should target the oxide ore in areas showing high Ba anomalies. On the other hand, exploration for Cu should target the sulfide zone, below the oxidation boundary, where primary copper sulfides and sulfosalts (e.g., chalcopyrite, enargite, tennantite) and secondary copper sulfides (e.g., chalcocite, covellite) are present.
Statistical calculations carried out in this study show the potential of the correlation factors between different trace elements to target and distinguish different ore zones with different metallurgical properties. This methodology may be applicable to other deposits in similar geologic environments elsewhere.











 nueva página del texto (beta)
nueva página del texto (beta)


