Introduction
Species of Echinostoma Rudolphi, 1809 (Echinosto matidae: Echinostomatinae) are frequently found in gastro-intestinal tract of a wide range of aquatic birds and mammals. To date, in South American birds 24 species of Echinostoma are known, from which only 4 have been described in Argentina: Echinostoma revolutum “group” in Sturnus vulgaris L. (Passeriformes), Echinostoma parcespinosumLutz, 1924 in Pardirallus maculatus (Boddaert) and Pardirallus sanguinolentus (Swaison) (Gruiformes), Echinostoma mendax Dietz, 1909 in Cygnus melancoryphus (Molina) (Anseriformes) and Echinostoma chloephagaeSutton and Lunaschi, 1980 in Chloephaga picta leucoptera (Gmelin) (Anseriformes) (Boero et al., 1972; Fernandes et al., 2015; Martorelli, 1987; Sutton & Lunaschi, 1980; Valente et al., 2014). Furthermore, in South American mammals 7 species occur, from which 3 have been reported in rodents from Argentina: Echinostoma revolutum (Froelich, 1802) in Myocastor coypus Molina, Echinostoma platensisSutton and Lunaschi, 1994 in Scapteromys aquaticus Thomas and Echinostoma rodriguesi Hsu, Lie and Basch, 1968 in Rattus norvegicus Berkenhout (Martínez, 2003; Martínez & Binda, 1993; Navone et al., 2009; Sutton & Lunaschi, 1994).
The objective of this paper is to describe 2 new species of Echinostoma recovered from the intestine of birds from Buenos Aires and Formosa Provinces, Argentina.
Material and methods
Six specimens of Guira Cuckoo, Guira guira (Gmelin) collected in La Marcela farm (26°17’35” S, 59°08’38” W), Pirané, Formosa Province, Argentina, were examined. Birds were dissected in the field and their viscera immediately analyzed after capture. The digeneans were recovered alive, fixed in 5% hot formalin, stained with hydrochloric carmine, and mounted in Canada balsam. Additionally, 7 digenean specimens identified as Echinostomatidae in the Helminthological Collection of Museo de La Plata (MLP-He) from the intestine of the Wattled Jacana, Jacana jacana (L.), from Punta Blanca, Buenos Aires Province, Argentina (34°57’ S, 57°40’ W), were studied. Measurements are given in micrometers (µm) unless otherwise stated, as the range followed by mean in parentheses. Drawings were made with the aid of a drawing tube. The digeneans obtained from G. guira were deposited in the MLP-He, and the hosts in the Ornithological Collection of the Museo de La Plata (MLP), La Plata, Argentina.
The following abbreviations were used: AT- anterior testis; CS- cirrus-sac; DVS-O- length of uterine field as distance between posterior margin of ventral sucker and ovary; PTF- post-testicular field as distance between posterior margin of posterior testis and posterior extremity of body. E- egg; Fb- forebody length; OeL- oesophagus length; OS- oral sucker; Ov- ovary; Ph- pharynx; PL-prepharynx length; PT- posterior testis; VS- ventral sucker; VS/OS- sucker width ratio. The term forebody is used according Manter (1970) as the distance between anterior end of body and the anterior edge of the ventral sucker. In addition, the following relative proportions were calculated after Kostadinova (2005): BW%, maximum body width as a proportion of body length; FO%, length of forebody as a proportion of body length; T%, length of post-testicular field as a proportion of body length; U%, length of uterine field as a proportion of body length.
Description
Echinostoma guirae n. sp. (Figs. 1-3; Table 1)

Figures 1-3 Echinostoma guirae n. sp. from Guira guira. 1, Entire worm, holotype, ventral view. Scale bar = 500 µm; 2, head-collar, paratype. Scale bar = 200 µm; 3, cirrus-sac, holotype. Scale bar = 200 µm.
Table 1 Comparative measurements of Echinostoma guirae n. sp. with related species.
| Species |
Echinostoma guirae n. sp. |
Echinostoma uncatum | Echinostoma crotophagae | ||
| Source | Present study | Dietz (1910) | Lutz (1925) | Gomez de Faria (1909) | Rodrigues & Rodrigues (1981) |
| Hosts | Natural Guira guira |
Natural Crotophaga major; Crotophaga ani |
Natural C. ani; Piaya cayana |
Natural Crotophaga major |
Natural Guira guira |
| Country | Argentina | Brazil | Venezuela | Brazil | Brazil |
| Bl (mm) | 4.1-5.6 | up to 10.5 | 19.5 | 3-8 | 9.1-13.6 |
| Bw (mm) | 0.743-1.0 | --- | --- | 1.0-1.9 | 1.1-2.1 |
| Hcl | 251-387 | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| Hcw | 386-531 | 520 | --- | --- | --- |
| Cs | 35 | 35 | 35 | 32-36 | 32-34 |
| Lateral single, | All in double row | ??? | All in single row | All in single row | |
| dorsal double | |||||
| As | 59-90 × 17-21 | 102-129 × 24-26 | --- | 134-160 × --- | --- |
| Ls | 71-83 × 17-19 | 75-95 × 16-22 | --- | --- | --- |
| Ds | 60-79 × 17-19 | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| OS | 106-140 × 121-155 | 220 × 170 | --- | 120-184 × 152-226 | 153-219 × 146-213 |
| VS | 561-793 × 445-561 | 480-780 × 460-570 | --- | 764-1,110 × 420-770 | 833-1,270 × 850-1,330 |
| VS/OS | 1: 3.6-3.7 | 1: 2.7-3.4* | --- | 1: 2.8-3.4* | 1: 4.3-6.2 |
| PL | 0-53 | 34 | --- | --- | 46-66 |
| Ph | 130-164 × 72-126 | 200-220 ø | --- | 192-228 × 160-222 | 166-266 × 153-233 |
| OeL | 314-396 | 170-200 | --- | --- | 190-410 |
| CS | 416-483 × 290-314 | --- | --- | --- | 660-1,330 × 249-399 |
| AT | 483-609 × 338-387 | 980-1,300 × 440-560 | --- | 600-680 × 410-444 | 616-1,460 × 330-660 |
| PT | 609-677 × 319-362 | --- | 630-790 × 400-410 | 583-1,460 × 230-580 | --- |
| Ov | 203-217 × 242-271 | 300-350 × 270 | --- | 280-290 ø | 166-453 × 166-506 |
| E | 82-97 × 48-53 | 86-91 × 50-53 | --- | 102 × 50 | 93-113 × 39-59 |
| Fb | 745-919 | --- | --- | --- | 958* |
| DVS-O | 0.706-1.04 mm | --- | --- | --- | 1.87 mm |
| PTF | 1.6-1.7 mm | --- | --- | --- | 2.7 mm* |
| BW% | 15-19 | 20* | --- | 18* | 18* |
| FO% | 13-17 | 8* | --- | 15* | 10* |
| U% | 15-19 | 27* | --- | 24* | 19* |
| T% | 29-31 | 22* | --- | 24* | 27* |
* Calculated from original descriptions or estimated from the published drawing.
Description based on 7 specimens: Body elongate (BW% = 15-19), with almost parallel margins, 4.1-5.6 (5.2) mm long by 743-1000 (886) wide. Forebody short 745-919 (767) in length (FO% = 13-17). Tegument armed with triangular scale like spines, arranged in transverse rows, less dense in hindbody, extending to level of posterior testis.
Head collar reniform, well developed, muscular, 251-387 long by 386-531 wide (316 × 441). Collar spines large, 35 in number; with following arrangement: 4 angle spines on each lappet (2 ventral and 2 dorsal), 59-90 × 17-21; 8 lateral spines in single row on each side, 71-83 × 17-19, and 11 dorsal spines in double row, 60-79 × 17-19. This collar spines can be included in the third model proposed by Kanev et al. (2009), i.e., 4 angle spines on each side, 10 lateral spines on each side, 2 additional spines on each side and 3 mid-dorsal spines (1 oral-sinistra, 1 aboral-central, 1 oral-dextra), i.e. [4+10+2+3+2+10+4] (Fig. 2).
Oral sucker ventro-subterminal, spherical, muscular, 106-140 × 121-155 (127 × 140). Ventral sucker well developed, muscular, cup-shaped, with deep cavity, located in the first quarter of body, 561-793 × 445-561 (708 × 513). Sucker width ratio 1: 3.6-3.7 (3.6). Prepharynx short, 0-53 (26); pharynx muscular, elongate, longer than oral sucker, 130-164 × 72-126 (153 × 104). Ratio of oral sucker width to pharynx width 1: 1.2-1.4 (1.3). Oesophagus 314-396 (349) long. Intestinal bifurcation closer to ventral sucker; caeca blind, overlapped by vitelline follicles, reaching fairly close to posterior extremity of body.
Testes 2, tandem, elongate-oval, irregular in outline, contiguous or slightly separated, located in the third quarter of body; anterior testis, 483-609 × 338-387 (544 × 354); posterior testis, 609-677 × 319-362 (638 × 340). Post-testicular field long, 1.6-1.7 mm. (T% = 29-31). Cirrus-sac elongate-oval, located dorsally, between anterior margin and mid-level of ventral sucker, 416-483 × 290-314 (445 × 298), contains internal seminal vesicle with saccular posterior portion and elongate anterior portion, strongly developed pars prostatica; pars prostatica well developed; cirrus tubular and unspined (Fig. 3). Genital pore median, anterior to ventral sucker.
Ovary small, entire, slightly transversely oval, located second quarter of body, 203-217 × 242-271 (211 × 256). Mehlis’gland median, contiguous with ovary, 193-285 × 285-290 (238 × 288). Laurer’s canal short. Uterus short, intercaecal, 0.706-1.04 mm (U% = 15-19). Metraterm long, muscular. Eggs numerous, 82-97 × 48-53 (90 × 49). Ratio of egg length to body length 1: 57-68. Vitellarium follicular, forming 2 lateral non-confluent fields, located between posterior margin of ventral sucker to near posterior extremity of body. Excretory vesicle Y-shaped; pore terminal.
Taxonomic summary
Type-host: Guira guira (Gmelin) (Cuculiformes, Cuculidae).
Site of infection: intestine.
Type-locality: La Marcela farm (26°17’35” S, 59°08’38” W), Pirané, Formosa Province, Argentina.
Date of collection: May 2005, September 2009, April 2015.
Specimens studied: holotype MLP-He 7206; paratypes MLP-He 7207 (6 specimens).
Prevalence: 50%.
Mean intensity: 3.
Etymology: the specific name, “guirae” refers to the specific name of the host.
Remarks
In the Neotropical Region, 4 species possessing 35 collar spines as the new species described herein have been recorded: Echinostoma discinctum Dietz, 1909, Echinostoma uncatum Dietz, 1909, Echinostoma crotophagae Gomes de Faria, 1909 and Echinostoma parvum Lutz, 1925.
Echinostoma discinctum, parasite of Cacicus solitarius Vieillot (Passeriformes, Icteridae) from Brazil (Dietz, 1910), was considered as member of Echinoparyphium Dietz 1909 by Yamaguti (1971); we agree with the last author because the collar of this species has 35 spines arranged in a double row. Based on this trait we separate it of E. guirae n. sp.
Echinostoma uncatum has been reported in cuculid birds: Crotophaga major Gmelin and Crotophaga ani L. from Brazil and Piaya cayana (L.) and C. ani from Venezuela (Dietz, 1910; Lutz, 1925; Travassos, 1922). This species has been described and illustrated by Dietz (1910) with 35 spines, 27 arranged all in double row and 4 angle spines on each side. This species differs of E. guirae n. sp. by the arrangement of collar spines and in most metrical characters and relative proportions showed in Table 1.
Echinostoma crotophagae has been described by Gomes de Faria (1909) parasitizing C. major from Brazil. Viana (1924) listed this species as synonym of E. uncatum, without any discussion, probably because it was described parasitizing C. major from the same country. Travassos et al. (1969) and Fernandes et al. (2015) considered both species as synonyms. Yamaguti (1971) maintained as a valid species to E. crotophagae. We agree with the last author because the collar was described with 32-36 collar spines all in single row, while E. uncatum was described with collar spines arranged all in double row. Furthermore, Rodrigues and Rodrigues (1981) studied specimens of E. uncatum from G. guira deposited of the Helminthological Collection of the Oswaldo Cruz Institute (CHIOC) and described 32-34 collar spines in a single row. We regarded these specimens belonging to E. crotophagae because both species have a similar arrangement of collar spines. This species mainly differs from E. guirae n. sp. by the arrangement of collar spines. Also differs in most metrical characters and relative proportions (Table 1).
Lutz (1925) briefly described Echinostoma parvum based on young worms experimentally obtained in Columba livia Gmelin (Columbidae) from Venezuela. The description of this species is incomplete, because only mentioned the presence of 35 collar spines but their arrangement is not described or illustrated. Therefore, the comparison between E. parvum and E. guirae n. sp. was not possible.
The species of Echinostoma reported previously in Argentina can be easily distinguished from E. guirae n. sp. based on the different number of collar spines: E. platensis (39-42), E. mendax (37), E. revolutum (37), E. rodriguesi (37), E. chloephagae (36-37), and E. parcespinosum (31-33).
Considering the differences in the distribution and number of collar spines, a new species, Echinostoma guirae n. sp. is proposed.
Echinostoma jacanae n. sp. (Figs. 4-6; Table 2)
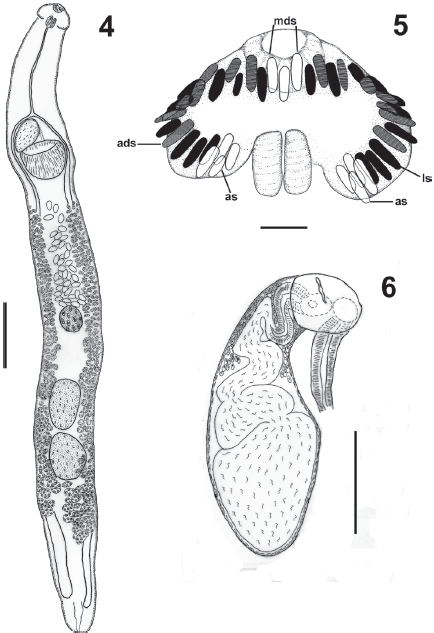
Figures 4-6 Echinostoma jacanae n. sp. from Jacana jacana. 4, Entire worm, holotype, ventral view. Scale ba r = 500 µm; 5, head-collar, holotype. Scale bar = 50 µm; 6, cirrus-sac, paratype. Scale bar = 100 µm. References: ads-additional spines; as-angle spines; ls-lateral spines; mds-mid-dorsal spines.
Table 2 Comparative measurements of Echinostoma jacanae n. sp. with related species.
| Species |
Echinostoma jacanae n. sp. |
Echinostoma siticulosum | Echinostoma exile |
Echinostoma attenuatum |
|
| Source | Present study | Dietz (1910) | Kohn and Fernandes (1975) | Alves-Pinto and Melo (2012) | Lumsden and Zischke (1963) |
| Hosts | Natural Jacana jacana |
Natural Crypturellus undulatus Crypturellus variegatus Crypturellus noctivagus |
E×perimental Columba livia Porphyrio martinicus |
E×perimental Columba livia |
Natural Rallus elegans Rallus longirostris |
| Country | Argentina | Brazil | Brazil | Brazil | USA |
| Bl (mm) | 3.83-5.20 | 5.5-7.5 | 2.89-5.91 | 4.56-6.93 | 7.22-11.2 |
| Bw | 355-486 | 700-940 | 630-900 | 702-1,390 | 885-1,590 |
| Hcl | 179-198 | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| Hcw | 238-271 | 430-480 | --- | --- | 425-743 |
| Cs | 45 | 41, 43, 45 | 43-45 | 45 | 45 |
| As | 33-38 × 10 | 60-115 × 19-26 | 21-54 × 9-14 | 40-50 × --- | 53-106 × 14-28 |
| Ls | 45 × 10-12 | 74-95 × 14-20 | 56-95 × 14-22 | --- | --- |
| Ds | 38-41 × 11-12 | 53-87 × 14-20 | --- | --- | --- |
| OS | 55-71 × 88-112 | 170-200 × 140-150 | 90-120 × 90-140 | 116-150 × 123-171 | 166-256 × 140-256 |
| VS | 242-329 × 242-333 | 560-590 × 470-500 | 460-620 × 400-760 | 409-717 × 430-717 | 0.673-1.333 mm |
| VS/OS | 1: 2.8-3.8 | 1: 3.3-3.4* | 1: 3.2-5.1 | 1: 3.5-4.2* | 1: 3.6 |
| PL | 45-60 | 60-170 | --- | --- | short |
| Ph | 69-93 × 69-90 | 116-130 × 88-102 | 90-130 × 90-110 | 89-184 × 61-137 | 128-217 × 102-153 |
| OeL | 604-807 | 530-570 | 130-230 | 205-239 | 243-448 |
| CS | 193-386 × 101-169 | 308-492 × 215-292 | 190-500 × 110-200 | 102-211 × 177-375 | 371-896 × 153-425 |
| AT | 290-413 × 174-244 | 830-1350 × 215-385 | 210-700 × 150-350 | 389-819 × 212-375 | 814-1345 × 212-566 |
| PT | 309-483 × 174-290 | 190-730 × 130-320 | 382-887 × 191-321 | 956-1,593 × 177-531 | |
| Ov | 152-246 × 121-217 | 260-380 × 200-370 | 60 -310 × 160-220 | 116-320 × 116-375 | 204-422 × 179-435 |
| E | 82-97 × 48-59 | 94-103 × 50-55 | 93-121 × 56-65 | 101-111 × 63-75 | 90-115 × 50-67 |
| Fb (mm) | 0.91-1.29 | --- | 0.525-0.659* | --- | 0.512-1.097 |
| DVS-O (mm) | 0.754-1.13 | --- | 1.08-1.25* | --- | 1.1-1.95 |
| PTF (mm) | 0.75-1.16 | --- | 1.40-1.43* | --- | 2.52* |
| BW% | 9-11 | 13* | 14-16* | --- | 11.9* |
| FO% | 22-25 | 17* | 10-12* | --- | 9.4* |
| U% | 20-25 | 22* | 20-23* | --- | 15* |
| T% | 19-24 | 12* | 25-26* | --- | 36* |
* Calculated from original descriptions or estimated from the published drawing.
Description based on 7 specimens: Body small, elongate, (BW% = 9-11), with maximum width at level of ventral sucker, 3.8-5.2 (4.5) mm long by 355-486 (432) wide. Forebody long, 909-1286 (1057) (FO% = 22-25). Tegument armed with spines.
Head collar reniform, well developed, 179-198 long by 238-271 wide (187 × 258), bearing 45 spines of similar size, with following arrangement: 4 angle spines on each lappet (2 ventral and 2 dorsal), 33-38 × 10; 3 lateral spines in single row on each side, 45 × 10-12, and 31 dorsal spines in double row, 38-41 × 11-12. This collar spines can be included in the eighth model proposed by Kanev et al. (2009), i.e. 4 angle spines on each side, 10 lateral spines on each side, 7 additional spines on each side, 3 mid-dorsal spines (1 oral-sinistra, 1 aboral-central, 1 oral-dextra), i.e. [4+10+7+3+7+10+4] (Fig. 5)
Oral sucker ventro-subterminal, 55-71 × 88-112 (65 × 96). Ventral sucker well developed, muscular, spherical, with shallow cavity, located between first and second quarter of body, 242-329 × 242-333 (291 × 286). Sucker width ratio 1: 2.8-3.8 (1: 3.3). Prepharynx short 45-60 (55); pharynx, muscular elongate-oval, 69-93 × 69-90 (79 × 75); oesophagus long, 604-807 (691); intestinal bifurcation anterior to ventral sucker; caeca blind, overlapped by vitelline follicles, reach fairly close to posterior extremity of body. Ratio of oral sucker width to pharynx width 1: 1.2-1.3.
Testes 2, tandem, smooth, elongate-oval, slightly separated; anterior testis, 290-413 × 174-244 (341 × 216); posterior testis, 309-483 × 174-290 (382 × 222). Post-testicular field long, 754-1160 (944) (T% = 19-24). Genital pore median, post-bifurcal. Cirrus-sac elongate-oval, located dorsally between level of intestinal bifurcation and anterior margin of ventral sucker, 193-386 × 101-169 (265-138), contains simple elongate seminal vesicle, pars prostatica, and cirrus with smooth surface (Fig. 6).
Ovary small, entire, oval, just pre-equatorial 152-246 ( 121-217 (205 × 176). Mehlis’ gland median, contiguous with ovary. Laurer's canal short, opening on dorsal surface immediately posterior to ovary. Uterus intercaecal, long, 0.754-1.13 (0.969) mm (U% = 20-25). Metraterm weakly-muscular. Eggs numerous, 82-97 × 48-59 (88 × 51). Ratio of egg length to body length 1: 44-97 (66). Vitellarium follicular, forming 2 lateral non-confluent fields of large and small follicles overlapping caeca; fields extend from to about half distance between ventral sucker and ovary to near posterior extremity of body.
Excretory vesicle not seen; excretory pore terminal.
Taxonomic summary
Type-host: Jacana jacana (L.) (Charadriiformes, Jacanidae)
Site of infection: intestine
Type-locality: Punta Blanca (34°57’0” S; 57°40’0” W), Buenos Aires Province, Argentina.
Date of collection: September 1994.
Specimens studied: holotype MLP-He, 3729/1; paratypes MLP-He 3728/1 (1 specimen), 3729/2 (3 specimens); voucher specimens MLP-He 3729/3 (2 specimens).
Etymology: the specific name, “jacanae” refers to the specific name of the host.
Remarks
So far, 3 species belonging to Echinostoma with 45 collar spines have been described in American birds: Echinostoma siticulosum Dietz, 1909 found parasitizing tinamiform birds from Brazil, Crypturellus undulatus (Temminck) (as Tinamus u.), Crypturellus variegatus (Gmelin) (as Tinamus v.) and Crypturellus noctivagus (Wied-Neuwied) [as Tinamus ? n. (Max.)] (Dietz, 1910); Echinostoma exileLutz, 1924 described in Brazil basedon experimental hosts, Columba livia and Porphyrio martinicus (L.) (Rallidae) (Alves-Pinto & Melo, 2012; Kohn & Fernandes, 1975; Lutz, 1924); and Echinostoma attenuatumLumsden and Zischke, 1963 found parasitizing Rallus elegans Audubon, and Rallus longirostris Boddaert (Rallidae) from USA (Bates & Meade, 1972; Heard, 1970; Lumsden & Zischke, 1963; Underwood & Dronen, 1986).
Echinostoma exile has morphological characteristics compatible with E. jacanae n. sp.; however, differs in the arrangement of spines collar (5 angle spines on each side + 33 or 35 spines in a double row). Moreover, the specimens of E. exile described by Kohn and Fernandes (1975) and Alves-Pinto and Melo (2012) can be differentiated of the new species by having larger suckers, shorter oesophagus, larger eggs and shorter forebody (notably short vs. long) (Table 2).
Echinostoma attenuatum includes specimens with a collar spines similar to those of the specimens here studied, but differs by having a forebody notably short (FO%: 9.4 vs. 22-25), uterus short (U%: 15 vs. 20-25), post-testicular field very long (T%: 36 vs. 19-24), as well as the dimensions of body size, spines, suckers, oesophagus, cirrus sac, testes, and ovary (Table 2).
Echinostoma siticulosum was described by Dietz (1910) with 41, 43 or 45 spines; 4 angle spines on each side and the remaining (33, 35 or 37) arranged in a double row. Mendheim (1940) re-described these specimens finding 43 spines in most of them, 41 in two specimens, and not mentioned the existence of 45 collar spines; however, this author agrees with the distribution pattern provided by Dietz (1910). Echinostoma siticulosum mainly differs of E. jacanae n. sp. by the disposition of collar spines. Also differs in most metrical characters and relative proportions (Table 2).
Three other species of Echinostoma with 45 spines have been described in the Palaearctic, Oriental and Australasian Regions: Echinostoma australasianumNicoll, 1914, in Antigone rubicunda (Perry) (as Antigone australasiana) from North Queensland Australia, with collar spines arranged in two uninterrupted rows (see Nicoll, 1914); Echinostoma coromandumOdening, 1962 in Bubulcus ibis coromandus (Boddaert) from Berlin Zoological Garden, originally from India, with collar spines apparently in single row and 4 spines in each ventral lappet (see Odening 1962, Fig. 16b), and Echinostoma gotoi Ando and Ozaki, 1923 in anatid birds and mammals from Asia with collar spines in a double row, not interrupted, with 6 spines in each ventral lappet (see MacDonald, 1981, Fig. 31.24). These species can be easily differentiated from E. jacanae n. sp. by the arrangement of collar spines (a single row in E. coromandum and a double row in E. australasianum and E. gotoi).
Based on all these morphological and morphometric differences, a new species: Echinostoma jacanae n. sp., is proposed.
Discussion
Kostadinova (2005) characterized the genus Echinostoma by possessing a collar composed by 31-55 spines, with lateral spines arranged in single row, dorsal spines in double row and 5 angle spines on each side. Kanev et al. (2009) considered that the number of spines in this genus is uneven, varying among 31-51, with 4 angle spines; these authors consider that even number of spines in this genus reflect specimens with spines lost, retracted, or supernumerary. These last authors provided 11 arrangement models of collar spines, highlighting that these are identical in larval and adult forms.
The arrangement of collar spines in E. uncatum, E. crotophagae, E. exile, E. siticulosum, E. australasianum, E. gotoi and E. coromandum is different to that established by Kostadinova (2005) for Echinostoma. In E. uncatum, E. siticulosum, E. exile, E. gotoi and E. australasianum dorsal and lateral spines are disposed in a double row. This arrangement is similar to that provided by Kostadinova (2005) for Echinoparyphium. However, this genus is also characterized by having a forebody long to extremely long (FO% >20), a post-testicular field short (T% = 15-30), and a uterus short to very short (U% = 3-20), with few eggs. Therefore, further researches are necessary on these 4 species to evaluate its accurate taxonomic position, since some its relative proportions, does not correspond to the diagnosis of genus.
Echinostoma crotophagae and E. coromandum have an uninterrupted collar spines, with dorsal and lateral spines in a single row. Both characters of E. crotophagae are similar to those provided by Kostadinova (2005) for Longicollia Bykhovskaya-Pavlovskaya, 1954, but the remaining diagnostic traits differ considerably. Finally, the number and arrangement of collar spines of E. coromandum is not coincident with any genus of the family. Considering all the differences referred above respecting to the number and pattern of collar spines established for Echinostoma by Kostadinova (2005), we believe necessary further studies on them, in order to clarify their real taxonomic position.
Echinostoma parvum is here regarded as species inquirenda, given that only is mentioned the presence of 35 collar spines and the arrangement of collar spines is not described or illustrated.















