Introduction
The growing demand for energy, the depletion of fossil fuel sources, and global warming are some of the factors which have led to the search of renewable sources of energy. This is the case for biofuels such as bioethanol and biodiesel, used for transportation and derived from biological materials such as sugars, crops, vegetable oils, grain starch, lignocellulosic materials, and organic residues (Pandiyan et al., 2019). The possibility of producing bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials has been studied for more than half a century. It can be obtained from lignocellulosic biomass such as agricultural wastes, soft woods, hard woods, cellulose wastes, industrial by-products, and forest wastes (Chandel and Singh, 2011; Viikari et al., 2012). For instance, agricultural residues are raw materials that can be obtained on a large scale (Miret et al., 2016). Within these, straws is the largest primary agricultural residue that is generated after the harvest and processing of cereal grains such as maize, rice, wheat, barley, among others, and represents about 90 % of the plant, making them an attractive and low-cost raw material (Ghosh et al., 2017; Ge et al., 2017; Tian et al., 2018). Due to the abundance of this biomass; its renewable nature, and the fact that it is not competing with food production make second-generation bioethanol a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels (Chandel et al., 2018).
The most promising characteristic of plant biomass is its high polysaccharide content, about 75 %, which is a valuable source of fermentable sugars. Bioethanol can be obtained from the structural portion of biomass, mostly cellulose (40-60 %) and hemicellulose (20-40 %) (Prasad et al., 2015; Kaltschmitt, 2018). The process of bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass requires five sequential steps: pretreatment, enzymatic hydrolysis, fermentation, product separation, and purification (Mosier et al., 2005).
From the degradation of lignocellulosic biomass, whether through physical, chemical, or enzymatic pretreatments, it is possible to obtain simple sugars, mostly glucose and xylose, which can be fermented by a large variety of microorganisms to produce bioethanol (Rastogi and Shrivastava, 2017). Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the most widely used yeast on industry, and the most promising for lignocellulosic bioethanol production, due to its great ability to ferment glucose, its high tolerance to ethanol, and its resistance to inhibitors present in lignocellulosic hydrolysates (Muruaga et al., 2016). However, S. cerevisiae is only able to metabolize six-carbon sugars such as glucose, but not five-carbon sugars such as xylose. Both types of sugars are obtained in lignocellulosic hydrolysates after acid hydrolysis of hemicellulose (Van Vleet and Jeffries, 2009; Cai et al., 2012).
Xylose represents about 20-30 % of the lignocellulosic material. In order to carry out an efficient conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into bioethanol, the use of pentoses released from hemicellulose hydrolysis is of utmost importance. In nature, there are about 100 types of microorganisms that can metabolize this substrate (Ge et al., 2017; Martins et al., 2018). Yeasts from the Candida, Pichia, and Pachysolen genera are able to ferment xylose into ethanol, whether aerobically or anaerobically. These yeasts require oxygen for their growth and are able of producing ethanol in significant glucose concentrations (Rastogi and Shrivastava, 2017).
Currently, microbial transformation of pentoses has been recognized as one of the main research challenges for second-generation bioethanol production technology. Multiple sugars such as xylose, arabinose, galactose, mannose, and glucose are released from hemicellulose degradation in the presence of ferulic and acetic acids. There are several wild strains such as Pachysolen tannophilus, Pichia stipitis, C. tropicalis, and C. shehatae that are unable to ferment fiveand six-carbon sugars simultaneously. Another challenge is to find yeasts that are tolerant to the various disintegration products generated from thermal and chemical lignocellulosic biomass pre-treatments, which are limiting factors in the fermentation process (Selim et al., 2018). Martins et al. (2018) conducted a search for yeasts capable of fermenting synthe-tic xylose into ethanol, finding the C. tropicalis S4 strain which metabolizes 56 g/L of synthetic xylose to produce 6 g/L of ethanol. In addition, yeasts of the Candida and Wickerhamomyces genera are able to ferment sugars obtained from hydrolysis of pretreated sugarcane bagasse by steam explosion into ethanol; however, the strains show a preference for glucose, by consuming it almost entirely, but not for other sugars present in the hydrolysate (Bazoti et al., 2017). Similarly, Pichia kudriavzevii 2-KLP1 yeast is able to metabolize sugars obtained from the acid hydrolysate of agroindustrial residues such as wheat bran, sugarcane bagasse, rice husk, and sawdust (Elahi and Rehman, 2018).
On the other hand, although yeasts capable of fermenting xylose do not reach the ethanol production levels required for industrial application, they could support future studies on genetic modification of microorganism, mainly on S. cerevisiae. The search and characterization of genes involved in xylose metabolic routes, may enable this yeast species to simultaneously metabolize glucose and xylose (Novy et al., 2014; Moysés et al., 2016; Kobayashi et al., 2018). In addition, another current trend is the search for microorganisms that can use pentoses to produce alternative compounds with a high added value in bio-refinery systems of lignocellulosic materials, such as xylitol (Santana et al., 2018), organic acids (Novy et al., 2018), and isobutanol (Lange et al., 2017), among others.
Due to the importance on pentose usage obtained from lignocellulosic biomass degradation, the main objective of the present work is the isolation of yeasts capable to metabolize five-carbon sugars, mostly xylose. In addition, we evaluated the metabolic capacity of isolated yeast to utilize xylose obtained from the chemical degradation of agroindustrial residues (corn stover, wheat straw, and mango residues) for second- generation bioethanol production from these lignocellulosic substrates.
Materials And Methods
Material
The raw material used in this work was sugarcane molasses, pineapple peel, mango residues (peels and seeds), corn stover and wheat straw collected from Guasave, Sinaloa, Mexico and stored at room temperature. The raw material was cut into small strips (2-10 mm in length) and stored at 4 °C until further utilization. All chemicals were reagent grade and purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, USA).
Isolation and morphological identification of yeasts
Yeast strains were isolated from 150 mL natural sources (sugarcane molasses, pineapple peel and mango residues) supplemented with 1 g/L (NH4)2SO4 and 90 mg/L ampicillin; the pH was adjusted to 4.5 using orthophosphoric acid (10% v/v). The culture was incubated for 24 h at 30 °C, on an orbital shaker at 150 rpm. Samples were serially diluted and plated onto agar plates composed of (g/L): glucose as carbon source (10), agar (10), and yeast extract (1). Petri dishes were incubated at 30 °C for 24 h and pure cultures were spread on slanted agar, stored at 4 °C and sub-cultured at regular intervals (Ortiz-Zamora et al., 2009).
Microscopic observation of the isolated microorganisms was carried out under methylene blue staining. The selected yeasts isolates were evaluated according to the colonial morphology proposed by De Becze, 1956. Yeasts were cryopreserved at -70 °C for further analysis.
Preculture, culture conditions and selection of yeasts
The pre-culture was carried out in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask with 50 mL liquid mineral medium containing glucose. After inoculation, the Erlenmeyer flask was incubated at 30 °C for 12 h, and stirred at 150 rpm. Once the yeast collection was obtained, its growth was evaluated in a minimum culture medium containing 0.2 % of (NH4)2SO4, 0.5 % KH2PO4, 0.04 % MgSO4.7H2O and 0.1 % yeast extract, supplemented with 5 % glucose (p/v) as carbon source (Ortiz-Zamora et al., 2009). Isolates were incubated at 30 °C and 150 rpm, pH was adjusted to 4.5. The inoculation was 3 x 106 viable cells/mL. We selected those yeasts that showed the highest growth after 48 h of incubation.
Molecular identification of yeasts
Yeast genomic DNA was extracted using DNAzol (DNAzol®, Invitrogen Cat. No. 10503027, Cincinnati, OH, USA), following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Genomic DNA was suspended in 30 μL of ultrapure water. For DNA amplification of the complete internal transcribed sequences (ITS) of the rDNA region (its1-5.8SrDNA-its2) we used the primer sets ITS-1 (5´-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3´) and ITS4 (5´-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3´) (White et al. 1990). PCR was conducted in a reaction volume of 25.0 μL that included: 17.65 μL of ultrapure water, 2.5 μL of buffer, 0.75 μL of 50 μM MgCl2, 1.0 μL of each primer (10 μM) , 1 μL 10 mM dNTP mix, 0.1 μL (1 U) of Taq platinum DNA polymerase (Invitrogen, USA), and 1.0 μL of template DNA (10 ng). PCR was performed using the following conditions: an initial denaturing step at 94 ºC for 5 min; subsequently, 30 cycles consisting of 30 s at 94 ºC followed by 30 s at 60 ºC for annealing and 30 s at 72 ºC for extension; and a final extension step of 5 min at 72 ºC. PCR products were purified using the QIAquick PCR purification Kit (Qiagen®, Cat. No. 28106. Germantown, MD, USA) and sequenced bi-directionally. Sequences were compared in the Genbank database using the BLAST-N software and the Mega-Blast algorithm (NCBI-National Center for Biotechnology Information). The sequences obtained were deposited at the GenBank under accession numbers MK630208-MK630212.
Effect of carbon source (glucose and xylose)
The yeasts selected were evaluated in their ability to grow in glucose and xylose as a carbon source. Fermentations were performed in a basal medium containing (g/L): 1 yeast extract, and mineral salts (g/L): 8.0 KH2PO4, 5.0 (NH4)2SO4, and 1.0 MgSO4.7H2O (Ortiz et al., 2009). Three culture media supplements were evaluated: glucose (100 g/L), xylose (50 g/L) and a glucose-xylose mixture (50 g/L, ratio 1:1) for the five yeast selected. The fermentations were carried out in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask with 50 mL of culture medium. The inoculation was 3 x 106 viable cells/mL. The temperature incubation was 30 °C and agitation speed was regulated at 250 rpm at pH 4.5. The fermentation was monitored every 5 h.
Obtaining acid hydrolysates from agroindustrial residues
The agroindustrial residues (corn stover, wheat straw and mango residues) were submitted to an acid pretreatment to release fermentable sugars; the pretreatment conditions were optimized in previous studies of the workgroup. Corn stover, wheat straw and mango residues were washed and dried at 60 °C for 48 h, then the dry biomass was ground and sieved to a particle size of 1 mm (Sieve No18, ASTM Standard). Corn stover and wheat straw were pretreated with 1 % H2SO4 (v/v), liquid-solid ratio (RLS) 10:1 and 45 min reaction at 121 °C (Sumphanwanich et al., 2008). After pretreatment, the sample was filtered, separating the solid phase from liquid phase (acid hydrolysates) and kept for further analysis. The acid hydrolysate was adjusted to pH 5 with 10 % KOH (w/v). Obtained sugars were used as a carbon source for alcoholic fermentation. On the other hand, the acid pretreatment of the mango peel-seed mixture was carried out using 2 % H2SO4 (v/v), RLS 10:1 and 30 min of reaction at 121 °C. Similarly, the liquid obtained was use as a carbon source in the alcoholic fermentation. The concentration of reducing sugar was assayed by 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic (DNS) method (Miller, 1959).
Fermentation of acid hydrolysates of agroindustrial residues
For ethanol production, culture media were elaborated using the reducing sugar obtained from the acid hydrolysate of each of the agroindustrial residues as a carbon source. The culture media were supplemented with yeast extract as a source of nitrogen and mineral salts, adjusting the pH to 4.5 (Ortiz-Zamora et al., 2009).
The fermentations were carried out in 250 mL Erlen-meyer flasks with 50 mL of culture medium at 30 °C and 150 rpm. The yeasts were inoculated at a concentration of 6x106 viable cells/mL. Culture samples were taken through the fermentation time, and we quantified yeast growth, substrate consumption and ethanol production.
Analytical methods
Yeast growth was followed by measuring the optical density (DO) in culture media (620 nm) using a spectrophotometer UV-Vis (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and these measurements were correlated to cell dry weight. Cell number was counted under the microscope, using a Thoma cell counting chamber. Viability percentage was obtained using the methylene blue staining method (Lange et al., 1993).
The reducing sugar concentration was determined using the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) method (Miller, 1959). The concentrations of glucose, xylose, acetic acid, xylitol, ethanol, HMF, and furfural were measured by HPLC (Waters 2414) with a Shodex SH1011 column (Shodex, New York, NY, USA). The column was maintained at 55 °C, and the mobile phase was H2SO4 5 mM with a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min. All samples were filtered (0.45 μm membrane) and injected (20 μL) in refraction index detector (Waters 2414, Milford, MA, USA) equipped with automatic sampler.
Results And Discussion
Yeast isolation and selection
A collection of 161 microorganisms isolated from sugarcane molasses, pineapple peels, and corn stover was generated. Colonial morphology confirmation on each of the isolates agreed with that of yeasts. The 161 yeasts were grown in a minimal medium with 5 % glucose (w/v). Only five yeast isolates showed OD values (620 nm) above 1, while 97 % of them showed between 0.1 to 0.8 OD at 48 h of incubation (Table 1).
Table 1 Yeast selection from different substrates (cane molasses, pineapple peel and corn stover).
Tabla 1. Selección de levaduras a patir de diferentes
sustratos (melaza de caña, cáscara de piña y rastrojo de
maíz).
| Microorganism Number | Biomass (DO 620 nm) | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 95 | 0.0-0.2 | 59 |
| 46 | 0.2-0.4 | 29 |
| 13 | 0.4-0.6 | 8 |
| 2 | 0.6-0.8 | 1 |
| 5 | 0.8-1.0 | 3 |
Molecular identification of selected yeasts
The selected yeast isolates were CBE 002, 012, 024, obtained from pineapple peel samples, as well as CBE 043 and 159 from sugarcane molasses. The obtained sequences contained the partial 18S rDNA-ITS1-5.8S-ITS2-28S rDNA region of the five isolates. BLAST-N analysis revealed that sequences from the amplified rDNA region of isolates shared 100 % of identity with sequences of Candida intermedia (KX981200.1; isolate CBE 002; 389 nt), Wickerhamomyces anomalus (MG241527.1; isolates CBE 012 and 024; 617 nt), and C. parapsilosis (MK268154.1; isolates CBE 043 and 159; 520 nt), identifying the isolates as belonging to these species (Table 2).
Table 2 Molecular identification of isolated yeasts by the rDNA ITS region sequence comparison
using the Nucleotide BLAST program (BLAST-N).
Tabla 2. Identificación molecular de las levaduras
aisladas comparando las secuencias de la región ITS del ADNr usando
el programa Nucleotide BLAST (BLAST-N).
| Strain | Sequence Lengtha (bp) | Closest relative | Homology tob | Identityc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBE002 | 389 | Candida intermedia | KX981200.1 | 100 |
| CBE012 | 617 | Wickerhamomyces Anomalus | MG241527.1 | 100 |
| CBE024 | 617 | Wickerhamomyces Anomalus | MG241527.1 | 100 |
| CBE043 | 520 | Candida parapsilosis | MK268154.1 | 100 |
| CBE159 | 520 | Candida parapsilosis | MK268154.1 | 100 |
aSize in base pairs (bp) of the ITS rDNA region (18S rRNA partial, ITS1 complete, 5.8S rRNA complete, ITS2 complete, 18S rRNA partial) of the strains amplified with the universal primers ITS1 and ITS4.
bSequence with highest homology to our isolates
cPercentage of identical nucleotides in the sequence obtained from the ITS rDNA region and the sequence of the closest relative found in the GenBank database.
A large amount of research has been carried out in recent years to genetically modify the S. cerevisiae model microorganism for the efficient use of xylose and arabinose (Subtil and Boles, 2011; Vilela et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2017; Kobayashi et al., 2018), as well as to increase the resistance to inhibitors (Smith et al., 2014; Inokuma et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2017). However, there is little emphasis on microorganisms that are able to naturally metabolize pentoses, and even more in those that are able to ferment xylose into ethanol. Bioethanol is the main focus of the lignocellulosic biomass conversion, and to obtain fermentable sugars requires the hydrolysis of cellulose and hemicellulose. The study of yeasts that are capable of using pentoses, mainly xylose, becomes relevant (Bellasio et al., 2015). Yeast members of the Candida genus are widely reported as a xylose fermenter (Schirmer-Michel et al., 2008; Martins et al., 2018; Pérez-Cadena et al., 2018; Shariq and Sohail, 2018), as well as yeasts of the Pichia, Kluyveromyces (Mussatto et al., 2012) and Wickerhamomyces (Bazoti et al., 2017) genera.
Effect of carbon source (glucose and xylose)
Several types of sugars are present in the lignocellulosic biomass, so the economic profitability of ethanol production depends on the use of the maximum amount of sugars (Dubey et al., 2016). Assays were carried out to measure the growth capacity and sugar consumption of the selected isolates (C. intermedia CBE002, W. anomalus CBE012, and CBE024, C. parapsilosis CBE043, and CBE159) in glucose (100 g/L) and xylose (50 g/L), two of the main sugars released during biomass pretreatment. All isolates were able to metabolize glucose as a carbon source. Candida intermedia CBE002 was the one that showed the highest growth at 56 h of incubation, whereas C. parapsilosis CBE159, W. anomalus CBE012, and CBE024 showed a similar growth, reaching a biomass production of 6 g/L, 50% less than the growth reached by C. intermedia CBE002 (Figure 1A). The maximum specific growth rates of C. intermedia CBE002 were 0.15 h-1 in glucose medium and 0.12 h-1 in xylose medium, showing that growth in glucose was faster than in xylose. The growth specific rate in the other evaluated strain was 2-fold lower (μmax=0.06 h-1) than for C. intermedia CBE002 in xylose medium (Table 3). Whereas in glucose medium was slightly lower (μmax=0.12 - 0.11 h-1). With regards to substrate con-sumption, C. intermedia CBE002 and C. parapsilosis CBE159 strains consumed 65-70 % of glucose (Figure 1B), with C. intermedia CBE002 generating a higher biomass yield, 0.21 g/g of consumed glucose (Table 3). Even when glucose is a carbon source that is easy to metabolize for most yeasts, the five strains evaluated did not consume the substrate in its entirety after 72 h of incubation.
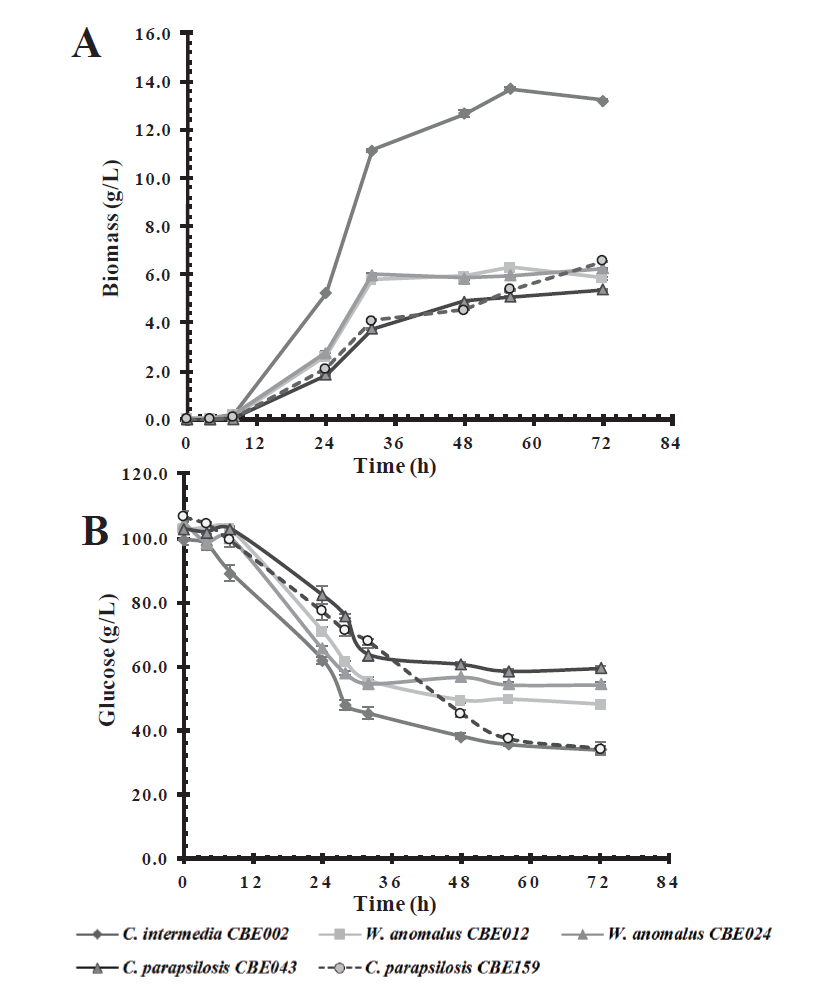
Figure 1 Effect of carbon source on biomass production (A) and glucose consumption (B) in a
basal medium by the five selected native yeast strains.
Figura 1. Efecto de la fuente de carbono en la
producción de biomasa (A) y el consumo de glucosa (B) en un medio
basal por las cinco cepas de levaduras nativas
seleccionadas.
Table 3 Effect of carbon source on maximum biomass (Xmax), specific growth rate
(μmax), yield (Yx/s) and substrate
consumption in five selected native yeasts.
Tabla 3. Efecto de la fuente de carbono en la biomasa
máxima (Xmax), tasa específica de crecimiento (μmax), rendimiento
(Yx/s) y consumo de sustrato en las cinco levaduras nativas
seleccionadas.
| Strain | Glucose (100 g/L) | Xylose (50g/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate comsuption | Biomass | Yield | Substrate consumption | Biomass | Yield | |||
| Sglu (g/L) | Xmax (g/L) | µmax (h-1) | YX/S (g/g) | Sxyl (g/L) | Xmax (g/L) | µmax (h-1) | YX/S (g/g) | |
| C. intermedia CBE002 | 65.52 | 13.70 | 0.150 | 0.21 | 27.58 | 9.71 | 0.125 | 0.35 |
| W. anomalus CBE012 | 54.66 | 6.28 | 0.123 | 0.11 | 20.83 | 4.64 | 0.069 | 0.22 |
| W.anomalus CBE024 | 50.36 | 6.25 | 0.123 | 0.12 | 22.82 | 4.12 | 0.063 | 0.18 |
| C. parapsilosis CBE043 | 43.50 | 5.38 | 0.115 | 0.12 | 24.32 | 4.22 | 0.066 | 0.17 |
| C.parapsilosis CBE159 | 72.35 | 6.55 | 0.115 | 0.09 | 26.07 | 4.26 | 0.060 | 0.16 |
Similarly, yeasts were able to grow in the basal culture medium containing xylose as a carbon source, showing a slower lag or adaptation phase (24 h) in comparison with the medium which contained glucose, at 8 h (Figure 2). Candida intermedia CBE002 showed a higher biomass yield (0.35 g/g of xylose), and reached a 9.71 g/L biomass at 72 h of incubation, twice the growth observed in the other selected strains (Table 3), similar to the results reported by Martins et al. (2018). The authors isolated thirty yeasts which were capable of consuming xylose as a carbon source; finding that Pichia guilliermondii G1.2 and G4.2 have the maximum biomass yield (0.3 g biomass/g xylose). However, we obtained the highest biomass productivity (0.13 g/L.h vs 0.09 g/L.h).
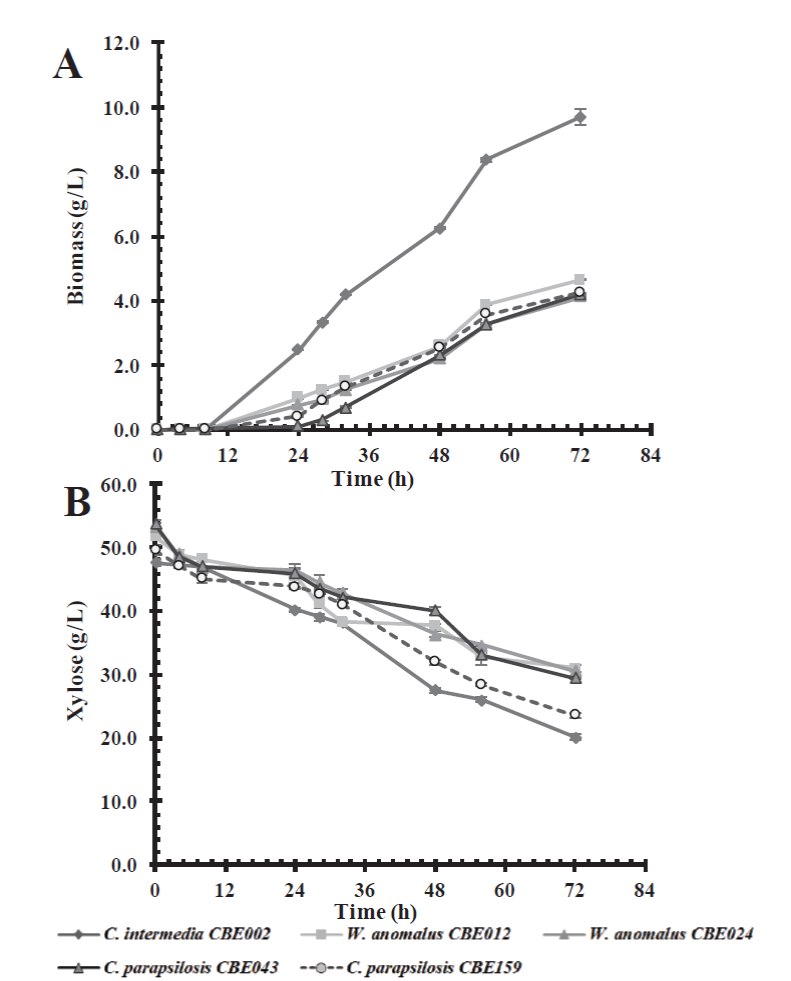
Figure 2 Effect of carbon source on biomass production (A) and xylose consumption (B) in a
basal medium by the five selected native yeast strains.
Figura 2. Efecto de la fuente de carbono en
la producción de biomasa (A) y el consumo de xilosa (B) en un medio
basal por las cinco cepas de levaduras nativas
seleccionadas.
On the other hand, assays conducted in a culture medium containing a mixture of glucose-xylose (50 g/L) in a 1:1 ratio; where C. intermedia CBE002 showed the greatest growth, reaching a biomass of 13 g/L after 72 h of incubation, followed by C. parapsilosis CBE043 and CBE159, both with similar growth profiles, reaching 7.5 g/L (Figure 3). Candida intermedia CBE002 was able to consume 80 % of the substrate, whereas the rest of the yeasts metabolized about 60 % of the substrate. Yeasts such as Pachysolen tannophilus, Pichia stipitis, C. tropicalis, and C. shehatae in their native state are not able to simultaneously metabolize pentoses and hexoses, as they show a preference for glucose over xylose. This is due to a repression mechanism which prevents the use of other carbon sources when glucose is available (Gancedo, 1998; Selim et al., 2018). This preference for glucose was observed in C. parapsilosis and W. anomalus isolated in this study, as opposed to that observed in C. intermedia CBE002, as this strain consumed both sugars at 72 h of incubation, i.e. it was able to metabolize xylose even in the presence of glucose, a desirable characteristic for bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass.
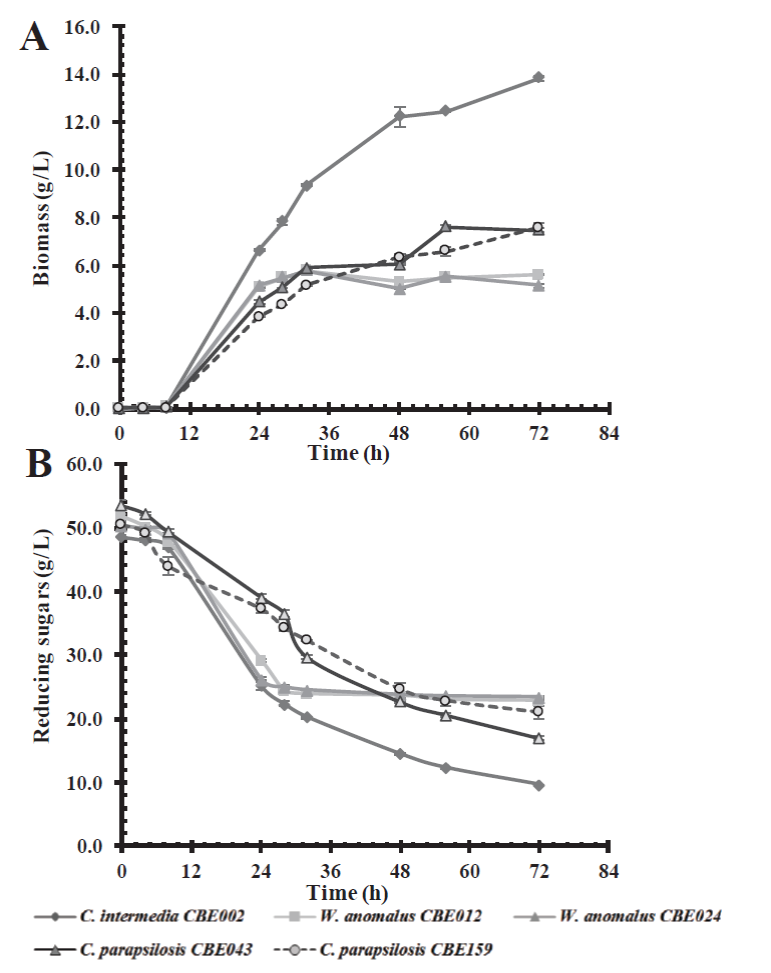
Figure 3 Effect of carbon source on biomass production (A) and consumption of an 1:1 mixture of
glucose:xylose (B) in a basal medium by the five selected native
yeast strains.
Figura 3. Efecto de la fuente de carbono en la producción de biomasa (A) y
el consumo de una mezcla de glucosa: xilosa, relación 1:1 (B) en un medio
basal por las cinco cepas de levaduras nativas seleccionadas.
Xylose catabolism occurs by three different metabolic routes in microorganisms. Most yeasts, excluding S. cerevisiae, uses the oxide-reductive route that involves two reactions. The first involves xylose reduction to xylitol by a NAD(P) H-dependent xylose reductase, secondly xylitol is oxidized to 5-xylulose by a NADP+- dependent xylitol dehydrogenase. Afterwards, 5-xylulose is phosphorylated to 5P-xylulose, which will be metabolized by the pentose phosphate route and glycolysis, as it occurs in the other metabolic routes (Moysés et al., 2016; Kwak and Jin, 2017). Pichia stipitis is capable of metabolizing xylose; however, there are restrictions when taking the substrate from the medium; the same occurs with S. cerevisiae, as it has a natural system of non-specific hexose transportation, which shows a low affinity for xylose. However, C. intermedia can grow well in a medium with xylose, as it has a high capacity to transport hexoses and pentoses by means of high and low-affinity transporters, through a facilitated diffusion mechanism which does not require high amounts of energy for substrate uptake, especially under scarce ATP production, and low oxygen conditions (Leandro et al., 2006). In this study, the most efficient strain in glucose and xylose assimilation, Candida intermedia CBE002, was selected to carry out fermentation assays from acid hydrolysates of different agroindustrial residues. Species members of the Candida genus have been reported as capable of fermenting xylose, possessing a xylose transportation system of high affinity, being tolerant to inhibitors, and producing ethanol from xylose (Gárdonyi et al., 2003). This suggest C. intermedia CBE002 is a promising strain for the use of sugars released from lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis in ethanol production, as well as for the isolation of genes involved in the use of xylose as a carbon source.
Fermentation of acid hydrolysates of agroindustrial residues
Fermentation assays were carried out using C. intermedia CBE002 in culture media containing sugars obtained from the acid hydrolysis of corn stover and wheat straw, and mango peel-seed residues. The liquid fraction collected after pretreatment with sulfuric acid of the various biomasses was used. Fermentation of the acid hydrolysates of corn stover was followed through time evaluating substrate consumption, biomass and ethanol production (Figure 4A). The culture medium with corn stover acid hydrolysates contained 26.4 g/L of total sugars, of which 51.5 % (13.6 g/L) is glucose, and 22.48 % (5.93 g/L) xylose. The biomass production was 11.4 g/L, depleting the two main carbon sources after 48 h fermentation, with a residual glucose and xylose concentration of 1.38 and 0.64 g/L, respectively. This strain consumed 17.62 g/L of total sugars, which belonged to glucose and xylose, so it was unable to metabolize other sugars present in the culture medium. As for ethanol production, the strain had an ethanol yield of 0.31 g/g of sugar consumed, reaching a 5.32 g/L concentration at a 24 h fermentation, obtaining a 0.22 g/L·h volumetric productivity, with a 60 % metabolic process efficiency (Table 4). The kinetic profile shows an etanol concentration of 4.78 g/L at 48 h fermentation, a lower concentration than the one quantified at 24 h. Regardless of the carbon source used, yeasts fermenting xylose require oxygen for growth, and do not produce enough ATP. Under aerobic conditions, even in the presence of xylose, yeasts use the ethanol produced as a carbon source to continue producing cell mass, CO2, and acetic acid. In this manner, ethanol production tends to first increase, followed by a decrease, and an increase in biomass yields (Rastogi and Shrivastava, 2017), which explains the behavior of C. intermedia CBE002, a strain that is capable of using ethanol as a carbon source, once the main sources have been depleted.
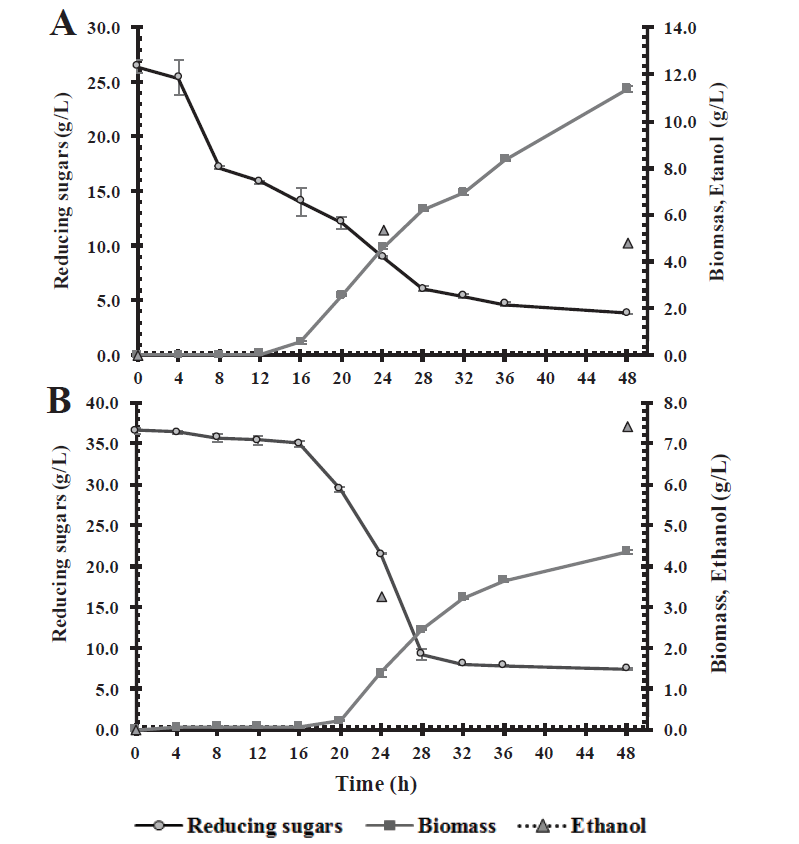
Figure 4 Kinetic profiles of biomass, substrate consumption and ethanol production of
C. intermedia CBE002 in acid hydrolysates of
corn stover (A) and mango seed-peel (B).
Figura 4. Pérfil cinético de biomasa, consumo de
sustrato y producción de etanol de C. intermedia CBE002 en
hidrolizados ácidos de rastrojo de maíz (A) y cáscara-semilla de
mango (B).
Table 4 Ethanol production and kinetic parameters by C. intermedia CBE002 in
acid hydrolysates of corn stover, mango residues and wheat straw as
carbon source.
Tabla 4. Producción de etanol y
parámetros cinéticos por C. intermedia CBE002 en hidrolizados ácidos
de rastrojo de maíz, residuos de mago y rastrojo de trigo como
fuente de carbono.
| Parameters | Corn stover | Mango (seed-peel) | Wheat Straw |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth specific rate -µmax (h-1) | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0 |
| Sugar consumed (g/L) | 17.62 | 29.17 | 0 |
| Production (g/L) | 5.32 | 7.42 | 0 |
| Yield-YEtOH/s (g/g) | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0 |
| Volumetric productivity-QEtOH | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0 |
| Conversion efficiency-դ(%)a | 60.00 | 51.00 | 0 |
aTheoretical yield for ethanol production defined at 0.51 g/g of substrate
Fermentation of the acid hydrolysates of mango peel-seed residues was followed by a kinetic profile of substrate consumption, biomass and ethanol production (Figure 4B). The acid hydrolysate culture medium of the mango peel and seed mixture contained 33.57 g/L of total sugars, of which 48.98 % (17.91 g/L) is glucose, and 17.91 % (6.23 g/L) xylose. Candida intermedia CBE002 was able to metabolize both carbon sources, leaving 1.82 and 1.63 g/L of residual glucose and xylose, respectively, consuming 79.76 % of total sugars. Yeast growth was lower than that observed in the corn stover acid hydrolysate, with a biomass concentration of 4.34 g/L at 48 h fermentation. In addition, a lower ethanol yield (0.26 g/g) was obtained, with a 0.15 g/L·h productivity and a 51 % process metabolic efficiency (Table 4). In accordance with the observations made in the kinetic profile, the lag phase is slower than in the acid hydrolysate of maize stubble, and there is no decrease in ethanol production at 48 h fermentation. This could be due to the higher sugar concentration in the culture medium, since a high sugar concentration causes a steady fermentation rate, in addition that the carbon source was not completely depleted (Mohd Azhar et al., 2017). Similarly, small xylitol traces are detected (data not showed), which may explain the lower ethanol yield, since it is necessary to oxidize xylitol to increase ethanol production in the metabolic route of xylose (Selim et al., 2018).
In both kinetic profiles (Figure 4) low ethanol yields (as compared to the theoretical ethanol yield of 0.51 g ethanol/g of substrate) and a lag or adaptation phase from 16 to 20 h were observed. This may be due to the fact that during lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment not only monomeric sugars are released, but also other compounds such as organic acids, furaldehydes (furfural and 5-hydroxymethyl furfural) and phenolic derivatives of lignin hydrolysis. Even when these compounds are found in small concentrations, they can inhibit the metabolism, extend the lag phase, damage cell membranes, and acidify the cytoplasm, reducing in this manner the ethanol yield and productivity (Moysés et al., 2016).
In addition, the fermentation of wheat straw acid hydrolysate was carried out. This contained 30.63 g/L of total sugars, where 54.04 % was glucose, and 30.54 % xylose. Although the culture medium had a carbon source available, C. intermedia CBE002 was unable to grow in this culture medium (data not shown). There are several factors inhibiting growth, as it was mentioned before, toxicity of some chemicals released during acid pretreatment can cause growth and cell production inhibition. In the acid hydrolysate of wheat straw, we detected a 1.4 g/L concentration of acetic acid, a by-product of hemicellulose deacetylation, a chemical compound not detected in acid hydrolysates of corn stover and mango peel-seed residues, which suggests that C. intermedia CBE002 is inhibited at this acetic acid concentration. The acetic acid from hemicellulose hydrolysis is relatively abundant with regards to other weak acids derived from lignocellulose, and has cytotoxic effects on yeast cells at high concentrations (Keating et al., 2006). In order to use this lignocellulosic substrate, further studies are required on acid pretreatment conditions and detoxification of the hydrolysates obtained.
Several studies have been carried out on bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass using yeast strains of the Candida genus. Moreno et al. (2019) evaluated fermentation by C. intermedia CBS 141442 strain of wheat stubble hydrolysates at different percentages in the culture medium, obtaining ethanol yields between 0.27 and 0.29 g/g. These ethanol yields are lower than those obtained in this study for the acid hydrolysate of maize stover (0.31 g/g) and similar to those obtained for mango peel-seed residues for C. intermedia CBE002 yeast. Similarly, they showed that by increasing the acid hydrolysate concentration of wheat stubble in the culture medium (50 %), C. intermedia CBS 141442 was completely inhibited in fermentation. In addition, C. pseudointermedia and Wickerhamomyces sp. were able to ferment sugarcane bagasse hydrolysates without detoxification, obtaining ethanol concentrations of 11 g/L at a 72 h fermentation, with a 0.15 g/L·h productivity (Bazoti et al., 2017). This is a lower value than that reported for corn stover (0.22 g/L·h), and similar to that obtained in mango peel-seed residues in this study.
Mussatto et al. (2012) carried out fermentations in acid hydrolysates of coffee industry wastes as raw materials (coffee silverskin: CS and spent coffee grounds: SCG) for ethanol production using S. cerevisiae, P. stipitis, and Kluyveromyces fragilis. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and P. stipitis showed the same ethanol yield (0.26 g/g). However, ethanol productivity (0.49 g/L.h) was higher for S. cerevisiae, suggesting that this strain had greater ability for ethanol production from sugar present in SCG hydrolysate (glucose, mannose, galactose and arabinose). Whereas that for CS hydrolysates, P. stipitis showed the faster and highest sugar consumption. This behavior may be related to the composition of culture medium. CS hydrolysate contains xylose (20 %), sugar that is not present in SCG hydrolysates, and only is metabolized for P. stipitis. The ethanol yield and productivity were low (0.11 and 0.04 g/L.h, respectively) compared to SCG hydrolysate. These results are thrice lower than those obtained in our work with C. intermedia CBE002 in acid hydrolysates of corn stover and mango peel-seed residues.
Candida intermedia CBE002 shows desirable characteristics for the bioethanol production process from lignocellulosic biomass, as this strain is able to metabolize glucose and xylose simultaneously during fermentation. Also, it produces ethanol from agroindustrial wastes, mostly in the acid hydrolysate of corn stover, this being a promising lignocellulosic substrate for bioethanol production on an industrial scale in northern Mexico. In addition, it is able to produce bioethanol from acid hydrolysates of mango by-products, a poorly studied raw material with great potential to be used in biorefineries. Due to the reported characteristics of CBE002, more in-depth studies are needed to understand the physiological and genetic importance of yeasts capable of fermenting xylose, which could serve as a gene reservoir for genetic modification of other microorganisms that do not have these characteristics, as well as helping the development of optimal biomass conversion processes, and establishing more cost-effective second-generation bioethanol production processes.
Conclusions
Five yeasts capable of metabolizing glucose and xylose were isolated from agroindustrial residues, molecularly identified and evaluated in their ability to grow in glucose and xylose as carbon source. C. intermedia CBE002 was the most promising strain for use in the fermentation of sugars obtained from lignocellulosic biomass degradation, as it is able to metabolize five and six-carbon sugars simultaneously, a desirable and rare characteristic in other yeast strains. In addition, C. intermedia CBE002 was able to produce ethanol from acid hydrolysates of corn stover and mango peel-seed. The kinetic parameters determined to obtain the best results with corn stover as carbon source: ethanol yield (YEtOH/s) of 0.31 g/g, ethanol productivity (QEtOH) 0.13 g/L.h, and metabolic efficiency of 60 %, making it an attractive strain to be used in second-generation bioethanol production from these agroindustrial residues, as it can ferment sugars from hemicellulose hydrolysis, achieving a more cost-effective production process.











 nueva página del texto (beta)
nueva página del texto (beta)


